gas washing bottle → boca ispiralica
Gas washing bottle or Drechsel bottle provide an inexpensive but effective method for washing or drying gases. The gas enters the bottle through the top of the central vertical tube, the lower end of which is below the surface of the washing medium. To maximize surface area contact of the gas to the liquid, a gas stream is slowly blown into the vessel through the fritted glass tip so that it breaks up the gas into many tiny bubbles. After bubbling through the medium, the gas rises to the top and exits through the side tube. It is named after the German chemist Edmund Drechsel (1843-1897).
germanium → germanij
Germanium was discovered by Clemens Winkler (Germany) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Germania meaning Germany. It is greyish-white semi-metal. Unaffected by alkalis and most (except nitric) acids. Stable in air and water. Germanium is obtained from refining copper, zinc and lead. Widely used in semiconductors. It is a good semiconductor when combined with tiny amounts of phosphorus, arsenic, gallium and antimony.
gold → zlato
Gold has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word aurum meaning gold. It is soft, malleable, bright yellow metal. Unaffected by air, water, alkalis and most acids. Gold is found in veins in the crust, with copper ore and native. Used in electronics, jewellery and coins. It is a good reflector of infrared radiation, so a thin film of gold is applied to the glass of skyscrapers to reduce internal heating from sunlight.
Goldschmidt process → Goldschmidtov postupak
Goldschmidt process (thermite process) is a method of extracting metals by reducing the oxide with aluminium powder. Practically all the metallic oxides are reducible by this method, the chief exception being the oxide of magnesium. The thermite process was developed by the German chemist Hans Goldschmidt (1861-1923) in 1893.
Goldschmidt was originally interested in producing very pure metals, but he soon realized the value in welding, a process known as Thermit welding.
vitamin → vitamin
The name vitamin is obtained from vital amines as it was originally thought that these substances were all amines. This is now known not to be true as vitamins have a range of structures. The body requires a small amout of vitamins, but any deficiency leads to metabolic and physical disorders.
volt → volt
Volt (V) is the SI derived unit of electric potential. One volt is the difference of potential between two points of an electric conductor when a current of 1 ampere flowing between those points dissipates a power of 1 watt. It was named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745-1827).
glucose → glukoza
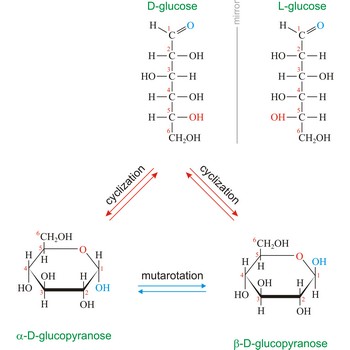
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
gravimetry → gravimetrija
Gravimetry is the quantitative measurement of an analyte by weighing a pure, solid form of the analyte. Since gravimetric analysis is an absolute measurement, it is the principal method for analysing and preparing primary standards.
A typical experimental procedure to determine an unknown concentration of an analyte in a solution is as follows:
- quantitatively precipitate the analyte from the solution
- collect the precipitate by filtering and wash it to remove impurities
- dry the solid in an oven to remove the solvent
- weigh the solid on an analytical balance
- calculate the analyte concentration in the original solution based on the weight of the precipitate.
weber → veber
Weber (Wb) is the SI derived unit of magnetic flux. The weber is the magnetic flux which, linking a circuit of one turn, produces in it an electromotive force of one volt as it is reduced to zero at a uniform rate in one second (Wb = V·s). The unit was named after the German scientist W.E. Weber (1804-1891).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Origin of the name Oukonunaka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table