galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
haematite → hematit
Haematite is a mineral of iron(III) oxide Fe2O3. It is the most important ore of iron and usually occurs in two main forms: as a massive red kidney-shaped ore and as grey to black metallic crystals known as specular iron ore. Haematite is the major red colouring agent in rocks; the largest deposits are of sedimentary origin. In industry haematite is also used as a polishing agent (jeweller’s rouge) and in paints.
ozonolisys → ozonoliza
Ozonolisys is a procedure of adding ozone to an unsaturated organic compound, by which first ozonides emerge, and then degrade.
PCl5 reaction → reakcija s PCl5
Reaction with phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is a characteristic of organic compounds containing a hydroxyl group and this reaction is used to identify these compounds in an organic analysis.
permeability → permeabilnost
Permeability (Latin permeare, to pass through) is a passage or diffusion of a gas, vapour, liquid, or solid through a material without physically or chemically affecting it.
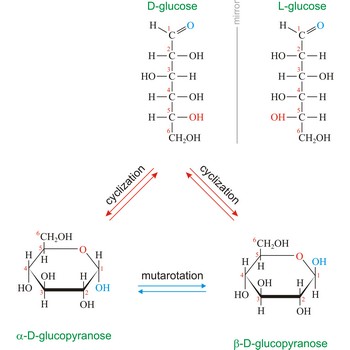
glucose → glukoza
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
halocarbon → halogenirani ugljikovodik
Halocarbon is a compound containing no elements other than carbon, one or more halogens, and sometimes hydrogen. The simplest are compounds such as tetrachloromethane (CCl4), tetrabromomethane (CBr4), etc. The lower members of the various homologous series are used as refrigerants, propellant gases, fireextinguishing agents, and blowing agents for urethane foams. When polymerized, they yield plastics characterized by extreme chemical resistance, high electrical resistivity, and good heat resistance.
petrochemicals → petrokemikalije
Petrochemicals are the industrially important organic chemicals which are derived from petroleum or natural gas.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organska kemija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table