osmium → osmij
Osmium was discovered by Smithson Tennant (England) in 1803. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word osme meaning smell. It is hard fine black powder or hard, lustrous, blue-white metal. Unaffected by air, water and acids. Characteristic acrid, chlorine like odour due to tetroxide compound. Osmium tetroxide highly toxic. Osmium is obtained from the same ores as platinum. Used to tip gold pen points, instrument pivots, to make electric light filaments. Used for high temperature alloys and pressure bearings. Very hard and resists corrosion better than any other.
Ostwald’s process → Ostwaldov proces
Ostwald’s process is a process by which the nitric acid can be obtained in three degrees. In the first stage ammonia and oxygen react (with platinum-rhodium as a catalyst), whereby the nitrogen monoxide and water emerge
In the second stage nitrogen monoxide reacts with oxygen whereby nitrogen dioxide emerges
and in the third stage nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water, in the presence of air, giving the nitric acid
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
palladium → paladij
Palladium was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (England) in 1803. Named after the asteroid Pallas which was discovered at about the same time and from the Greek name Pallas, goddess of wisdom. It is soft, malleable, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resists corrosion; dissolves in oxidizing acids. Absorbs hydrogen. Metal dust is combustible. Palladium is obtained with platinum, nickel, copper and mercury ores. Used as a substitute for silver in dental items and jewellery. The pure metal is used as the delicate mainsprings in analog wristwatches. Also used in surgical instruments and as catalyst.
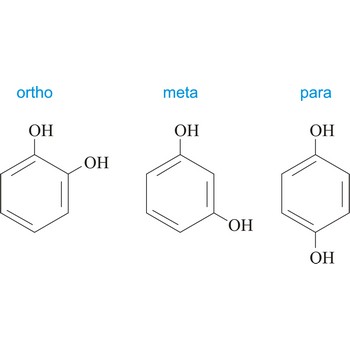
para position → para položaj
Para position in organic chemistry is the one in which there are two same functional groups tied to a ring of benzene in the position 1 and 4. The abbreviation p- is used, for example, p-Hydroquinone is 1,4-dihydroxybenzene.
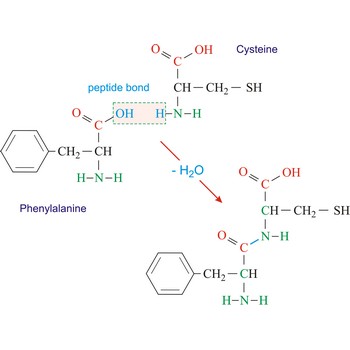
peptide bond → peptidna veza
Peptide bond emerges when two amino acid join in a way that the carbon atom from one connects with the nitrogen atom from the other (creating a C-N bond).
pH → pH
pH is a convenient measure of the acid-base character of a solution, usually defined by
where c(H+) is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per litre. The more precise definition is in terms of activity rather than concentration.
A solution of pH 0 to 7 is acid, pH of 7 is neutral, pH over 7 to 14 is alkaline.
phenylalanine → fenilalanin
Phenylalanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. It is quite hydrophobic and even the free amino acid is not very soluble in water. Phenylalanine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Phe, F
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 165.19 g/mol
pickling → dekapiranje
Pickling is a process to chemically remove scale or oxide from steel to obtain a clean surface. When applied to bars or coils prior to bright drawing, the steel is immersed in a bath of dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %) heated to a temperature of around 80 °C. An inhibitor is added to prevent attack and pitting of the cleaned metal. After pickling, a washing process takes place followed by immersion in a lime-water bath to neutralise any remaining acid.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organic acid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table