unsaturated hydrocarbon → nezasićeni ugljikovodik
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are organic compounds containing double (alkenes) or triple (alkynes) bonds in their molecules.
lead → olovo
Lead has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word plumbum meaning liquid silver. It is very soft, highly malleable and ductile, blue-white shiny metal. Tarnishes in moist air; stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in nitric acid. Compounds toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Danger of cumulative effects. Lead is found most often in ores called galena or lead sulfide (PbS). Used in solder, shielding against radiation and in batteries.
waste water → otpadna voda
Waste waters are waters which pour down from housing, public or industrial plants and are polluted with mineral and organic substances and microorganisms.
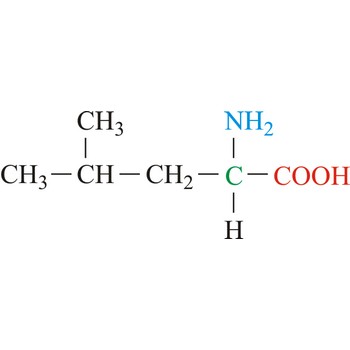
leucine → leucin
Leucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It has one additional methylene group in its side chain compared with valine. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Leucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Leu, L
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.17 g/mol
limestone → vapnenac
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate in the form of the mineral calcite.. Some 10 % to 15 % of all sedimentary rocks are limestones. Limestone is usually organic, but it may also be inorganic. Calcium carbonate may have been directly precipitated from the sea-water or by the lithification of coral reefs, marine organism shells, or marine organism skeletons.
lysine → lizin
Lysine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. Lysine is a base, as are arginine and histidine. The amino group is highly reactive and often participates in reactions at the active centers of enzymes. Lysine plays an important role in coordinating negatively charged ligands. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Lys, K
- IUPAC name: 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H14N2O2
- Molecular weight: 146.19 g/mol
weak electrolyte → slabi elektrolit
Weak electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions dissociate only partially, giving ions and which are in equilibrium with undissociated molecules. Their water solutions conduct electric current weakly. For example, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions, so that an acetic acid solution contains both molecules and ions.
white spirit → bijeli špirit
White spirit (mineral spirits, petroleum spirits) is a paraffin-derived clear, transparent liquid which is a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating.
Zimmermann-Reinhardt’s reagent → Zimmermann-Reinhardtov reagens
Zimmermann-Reinhardt’s reagent is a mixture of manganese(II) sulphate, sulphuric acid and phosphorus acid. It is used for preventing oxidation of chloride ion while titrating iron(II) ion with permanganate solution.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organic acid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table