condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
conformation → konformacija
Conformation is one of the very large numbers of possible spatial arrangements of atoms that can be interconverted by rotation about a single bond in a molecule. The conformation of a molecule is not fixed, though one or another shape may be more likely to occur. There are two extreme cases:
Staggered conformation (antiperiplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as far apart as possible from the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
Eclipsed conformation (syn-periplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as close as possible to the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
cracking → krekiranje
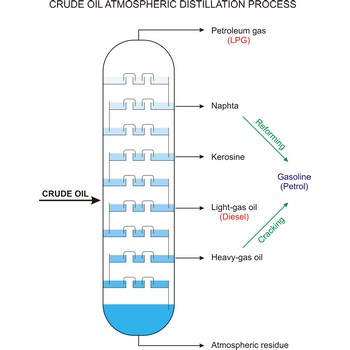
Cracking is the process whereby heavy molecules of petroleum or crude oil are broken down into hydrocarbons of lower molecular weight (especially in the oil-refining process).
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
inorganic chemistry → anorganska kemija
Inorganic chemistry, the branch of chemistry concerned with compounds of elements other than carbon. Certain simple carbon compounds, such as CO, CO2, CS2, carbonates CO32- and cyanides CN-, are usually treated in inorganic chemistry.
lactodensimeter → laktodenzimetar
Lactodensimeter is a special aerometer used for determining the density of milk.
low-weight fractions → lake frakcije
Low-weight (petroleum) fractions have low boiling points and short carbohydrates chains.
Curie → Curie
Maria Sklodowska-Curie (1867-1934) Polish-born French chemist who went to Paris in 1891. She married the physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906) in 1985 and soon began work on seeking radioactive elements other than uranium in pitchblende (to account for its unexpectedly high radioactivity). By 1898 she had discovered radium and polonium although it took her years to purify them. In 1903 the Curies shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Henri Becquerel, who had discovered radioactivity.
darmstadtium → darmstadtij
Darmstadtium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in November 1994. The title honours the Laboratory for Heavy Ion Research (called GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany, where the substance was first made. It is synthetic radioactive metal. The fusion-evaporation reaction using a 62Ni beam on an isotopically enriched 208Pb target produced four chains of alpha-emitting nuclides following the presumed formation of 269110 + 1n.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Određivanje starosti radioaktivnim ugljikom." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table