bromine → brom
Bromine was discovered by Antoine J. Balard (France) in 1826. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word bromos meaning stench. It is reddish-brown liquid with suffocating, irritating fumes. Gives off poisonous vapour. Causes severe burns. Oxidizer. Bromine occurs in compounds in sea water. It was once used in large quantities to make a compound that removed lead compound build up in engines burning leaded gasoline. Now it is primarily used in dyes, disinfectants and photographic chemicals.
Bunsen’s cell → Bunsenov članak
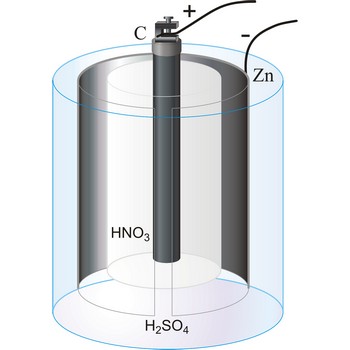
Bunsen’s cell is a primary cell devised by Robert W. Bunsen consisting of a zinc cathode immersed in dilute sulphuric acid and carbon anode immersed in concentrated nitric acid. The electrolytes are separated by a porous pot. The cell gives an e.m.f. of about 1.9 V.
covering power → prekrivna moć
Covering power is the ability of a plating solution under a set of specified plating conditions to deposit metal on the surfaces of recesses or deep holes. This term suggests an ability to cover, but not necessarily to build up, a uniform coating.
crystallisation → kristalizacija
Crystallisation is process in which the melted substance from a saturated solution turns into solid substance (crystal).
burette → bireta
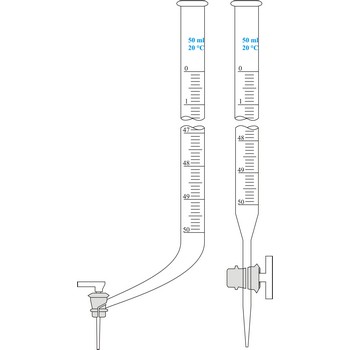
Burette is a graded glass pipe which on its lower side has a glass faucet by which it can drop a precise quantity of liquid. Inner diameter of a burette must be equal in its whole length, because the accuracy of volume measurement depends upon that. Burettes are primarily used in volumetric analysis for titration with standard solution reagent. Most often Schellbach’s burette is used, graded on 50 mL with division of scale on 0.1 mL. Every burette is calibrated on discharge. For serial determining automatic burettes are used.
cadmium → kadmij
Cadmium was discovered by Friedrich Strohmeyer (Germany) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cadmia meaning calamine (zinc carbonate, ZnCO3), or from the Greek word kadmeia with the same meaning. It is soft, malleable, blue-white metal. Tarnishes in air, soluble in acids, insoluble in alkalis. Boiling cadmium gives off a weird, yellow-colored vapour that is poisonous. Cadmium can cause a variety of health problems, including kidney failure and high blood pressure. Cadmium is obtained as a by product of zinc refining. The mayor use of cadmium is in electroplating of steel to protect it from corrosion. Also used to make nickel-cadmium batteries. The ability of cadmium to adsorb neutrons has made it of great importance in the design of nuclear reactors. Its compounds are found in paint pigments and a wide variety of intense colours.
carboxylic acids → karboksilne kiseline
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more RC(=O)OH groups (the carboxyl group). In the systematic chemical nomenclature carboxylic acids names end in the suffix -oic (e.g. ethanoic acids, CH3COOH). The carbon of the terminal group being counted as part of the chain. They are generally weak acids. Carboxylic acids include a large and important class of fatty acids and may be either saturated or unsaturated. There are also some natural aromatic carboxylic acids (benzoic, salicylic).
chemical equation → kemijska jednadžba
Chemical equation is a way of denoting a chemical reaction using the symbol for the participating particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.); for example,
The single arrow is used for an irreversible reaction; double arrows are used for reversible reactions. When reactions involve different phases, it is usual to put the phase in brackets after the symbol.
| s | = | solid |
| l | = | liquid |
| g | = | gas |
| aq | = | aqueous |
The numbers a, b, c, and d, showing the relative numbers of molecules reacting, are called the stoichiometric coefficients. The convention is that stoichiometric coefficients are positive for reactants and negative for products. If the sum of the coefficients is zero, the equation is balanced.
chlorine → klor
Chlorine was discovered by Carl William Scheele (Sweden) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chloros meaning pale green. It is greenish-yellow, disagreeable gas with irritating odour. Gas is toxic and severe irritant by contact or inhalation. Never found in free form in nature. Commercial quantities of chlorine are produced by electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride (NaCl) from seawater or brine from salt mines. Used in water purification, bleaches, acids and many, many other compounds such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFC).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nezasićena otopina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table