salt fog test → ispitivanje u slanoj komori
Salt fog test is an accelerated corrosion test in which specimens are exposed to a fine mist of a solution usually containing sodium chloride (typically 5 %). Other contaminants can be added according to desired conditions. It is mainly used to determine the effectiveness of material finishes and protective coatings on materials. Salt-fog testing is also used to determine the effects of salt deposits on the electrical functions of electronic assemblies.
sedimentary rocks → sedimentne stijene
Sedimentary Rocks are formed by the accumulation and subsequent consolidation of sediments into various types of rock. There are three major types of sedimentary rocks:
Biogenic sedimentary rocks are formed from organic processes when organisms use materials dissolved in water to build a shell or other skeletal structure.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed directly of the sediments or fragments from other rocks.
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed through evaporation of a chemical rich solution.
Based on their sizes, sediment particles are classified, based on their size, into six general categories:
- boulder (>256 mm)
- cobble (64 - 256 mm)
- gravel (2 - 64 mm)
- sand (1/16 - 2 mm)
- silt (1/256 - 1/16 mm)
- clay (<1/256 mm)
sedimentation → sedimentiranje
Sedimentation is a process of separating specifically heavier, suspended matter, than the solution is. Solid matter settles on the bottom of the vessel and the liquid above it is poured off. The settling zone is the largest portion of the sedimentation basin. This zone provides the calm area necessary for the suspended particles to settle. The sludge zone, located at the bottom of the tank, provides a storage area for the sludge before it is removed for additional treatment or disposal.
silver coulometer → srebrni kulometar
Silver coulometer consists of a platinum vessel which acts as a cathode and contains a solution of pure silver nitrate as an electrolyte (c(AgNO3) = 1 mol/L). A rod of pure silver enclosed in a porous pot acts as the anode. The current density at the anode should not exceed 0.2 Acm-2. After electrolysis, the electrolyte is taken out and the platinum vessel is washed, dried and weighed. The increase in the weight gives the amount of silver deposited (96500 C of electricity deposits 107.88 g of silver). From the mass of the silver deposited, the coulomb involved in the reaction can be calculated.
sol → sol
Sols are dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid. The particles may be macromolecules or may be clusters of small molecules. Lyophobic sols are those in which there is no affinity between the dispersed phase and the liquid (e.g. silver chloride dispersed in water). Lyophobic sols are inherently unstable, in time the particles aggregate, and form a precipitate. Lyiophilic sols, on the other hand, are more like true solutions in which the solute molecules are large and have an affinity for the solvent (e.g. starch in water). Association colloids are systems in which the dispersed phase consists of clusters of molecules that have lyophobic and lyophilic parts (e.g. soap in water).
solubility → topljivost
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a given quantity of solvent at a specific temperature. Generally, for a solid in a liquid, solubility increases with temperature; for a gas, solubility decreases. Common measures of solubility include the mass of solute per unit mass of solution (mass fraction), mole fraction of solute, molality, molarity, and others.
spectrophotometer → spektrofotometar
Spectrophotometer is an instrument for measuring the amount of light absorbed by a sample.
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
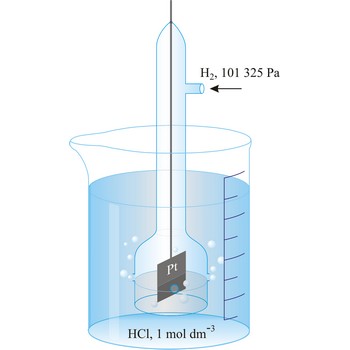
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
supercritical fluid → superkritični fluid
Supercritical fluid is any substance above its critical temperature and critical pressure (see phase diagram). It shows unique properties that are different from those of either gases or liquids under standard conditions. A supercritical fluid has both the gaseous property of being able to penetrate anything, and the liquid property of being able to dissolve materials into their components. Solublity increases with increasing density (i.e. with increasing pressure). An example of this is naphthalene which is practically insoluble in low pressure carbon dioxide. At 100 bar the solubility is 10 g/L and at 200 bar it is 50 g/L. Rapid expansion of supercritical solutions leads to precipitation of a finely divided solid.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nezasićena otopina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table