colloid mill → koloidni mlin
Colloid mills are machines used to grind aggregates into very fine particles or to apply very high shearing within a fluid to produce colloid suspensions or emulsions in which the particle sizes are less than 1 micrometer. One type of colloid mill is called a disc mill, in which a mixture of a solid and liquid (or two liquids) is passed between two discs a small distance apart, which rotate very rapidly relative to each other. Applications of colloid mills occur in food processing, in paint manufacture, and in the pharmaceutical industry.
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
composition of ocean water → sastav oceanske vode
The proportions of the major constituents of ocean water are almost constant throughout the world. Salinity (total salt content) and the concentrations of individual chemical constituents in sea wateris given the units psu (practical salinity units). For most purposes one can assume that the new unit, psu, and the older unit, ‰, are synonymous.
The average composition of the ocean water is as shown on the following table.
| Constituent | Percentage of total salt |
|---|---|
| Chlorine | 55.3 % |
| Sodium | 30.8 % |
| Magnesium | 3.7 % |
| Sulphur | 2.6 % |
| Calcium | 1.2 % |
| Potassium | 1.1 % |
critical point → kritična točka
In general, critical point is the point on the phase diagram of a two-phase system at which the two coexisting phases have identical properties and therefore represent a single phase. At the liquid-gas critical point of a pure substance, the distinction between liquid and gas vanishes, and the vapour pressure curve ends. The coordinates of this point are called the critical temperature and critical pressure. Above the critical temperature it is not possible to liquefy the substance.
cryoscopic constant → krioskopska konstanta
Cryoscopic constant (Ef) is the constant that expresses the amount by which the freezing point Tf of a solvent is lowered by a non-dissociating solute, through the relation
where m is the molality of the solute.
crystallisation → kristalizacija
Crystallisation is process in which the melted substance from a saturated solution turns into solid substance (crystal).
decomposing → raščinjavanje
Decomposing in analytical chemistry means that a certain substance is converted, by melting it with a suitable melting medium (sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, ...) in the kind of compound which will afterwards that dissolve in water, acid or base very easily.
critical temperature → kritična temperatura
Critical temperature is the temperature of the liquid-vapour critical point, that is, the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by an increase of pressure.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
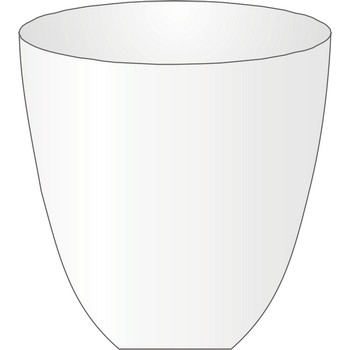
crucible → lončić za žarenje
Crucible is used for heating small amounts of solid in an oven to very high temperatures. Crucibles are usually made out of porcelain, platinum, nickel or iron.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nečista tvar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table