nitrogen → dušik
Nitrogen was discovered by Daniel Rutherford (Scotland) in 1772. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words nitron genes meaning nitre and forming and the Latin word nitrum (nitre is a common name for potassium nitrate, KNO3). It is colourless, odourless, generally inert gas. Minimally reactive at room temperature. A component of many organic and inorganic compounds. Makes up about 78 % of earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen is obtained from liquid air by fractional distillation. Primarily to produce ammonia and other fertilizers. Also used in making nitric acid, which is used in explosives. Also used in welding and enhanced oil recovery.
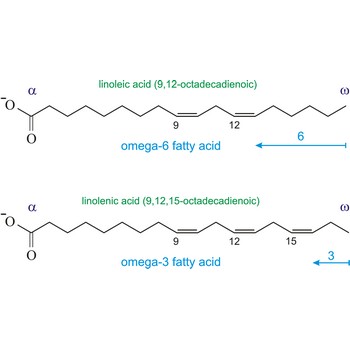
omega-3 fatty acids → omega-3 masne kiseline
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning they contain more than one double bond. The name omega-3 indicates that the first double bond occurs on the third carbon atom (n-3) from the methyl (-CH3) end of the molecule (omega position). The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3). ALA comes from plants. EPA and DHA come from fish.
Similarly, the first double bond in omega-6 fatty acids is located between the sixth and seventh carbon atom (n-6) from the methyl end of the fatty acid (omega end).
osmium → osmij
Osmium was discovered by Smithson Tennant (England) in 1803. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word osme meaning smell. It is hard fine black powder or hard, lustrous, blue-white metal. Unaffected by air, water and acids. Characteristic acrid, chlorine like odour due to tetroxide compound. Osmium tetroxide highly toxic. Osmium is obtained from the same ores as platinum. Used to tip gold pen points, instrument pivots, to make electric light filaments. Used for high temperature alloys and pressure bearings. Very hard and resists corrosion better than any other.
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
phosphorus → fosfor
Phosphorus was discovered by Hennig Brandt (Germany) in 1669. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word phosphoros meaning bringer of light. White phosphorus is white to yellow soft, waxy phosphorescent solid with acrid fumes. Toxic by inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Red phosphorus is powdery, non-flammable and non-toxic. Phosphorus is found most often in phosphate rock. Pure form is obtained by heating a mixture of phosphate rock, coke and silica to about 1450 °C. Used in the production of fertilizers and detergents. Some is used in fireworks, safety matches and incendiary weapons. Phosphorus is also important in the production of steels, phosphor bronze and many other products.
platinum → platina
Platinum was discovered by Antonio de Ulloa (South America) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the Spanish word platina meaning silver. It is rare, very heavy, soft, silvery-white metal. Resists oxygen and water. Platinum is produced from deposits of native, or elemental. Used in jewellery, to make crucible and special containers and as a catalyst. Used with cobalt to produce very strong magnets. Also to make standard weights and measures. Resists corrosion and acid attacks except aqua regia.
potassium → kalij
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word qali meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word kalium). It is soft, waxy, silver-white metal. Fresh surface has silvery sheen. Quickly forms dull oxide coating on exposure to air. Reacts strongly with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Reacts violently with oxidants. Occurs only in compounds. Potassium is found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3)·6H2O] and sylvite (KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapours in a special retort. Used as potash in making glass and soap. Also as saltpetre, potassium nitrate (KNO3) to make explosives and to colour fireworks in mauve. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissues.
praseodymium → praseodimij
Praseodymium was discovered by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1885. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words prasios didymos meaning green twin. It is silvery white, moderately soft, malleable, ductile metal. Reacts slowly with oxygen. Reacts rapidly with water. Metal ignites and burns readily. Praseodymium is obtained from same salts as neodymium. Used with neodymium to make lenses for glass maker’s goggles since it filters out the yellow light present in glass blowing. Alloyed with magnesium creates a high-strength metal used in aircraft engines. Misch metal, used in the manufacture of pyrophoric alloys for cigarette lighters, contains about 5 % praseodymium metal. (Typically composition of misch metal are Ce:Nd:Pr:La:Other rare earth=50:18:6:22:4).
protactinium → protaktinij
Protactinium was discovered by Otto Hahn (Germany) and Lise Meitner (Austria) in 1917. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word protos meaning first. It is very rare, silvery-white, extremely radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; reacts with oxygen and acids. Attacked by steam. Highly radiotoxic. Protactinium is extremely toxic and must be handled with great care. Protactinium does not occur in nature. Found among fission products of uranium, thorium and plutonium.
radium → radij
Radium was discovered by Marie and Pierre Curie (France) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word radius meaning ray. It is silvery-white radioactive metal. Reacts with oxygen and water. Highly radiotoxic. Carcinogen by inhalation, ingestion, or exposure. Radium is found in uranium ores at 1 part per 3 million parts uranium. Used in treating cancer because of the gamma rays it gives off.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Naruhodo meaning." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table