temperature → temperatura
Temperature is a measure to the average kinetic energy of its molecules. The SI unit in which thermodynamic temperature is expressed is the kelvin (K).
terminal → terminalni
Terminal in chemistry means: the end of a polymer molecule and a point at which electron connections can easily be made or broken.
unsaturated hydrocarbon → nezasićeni ugljikovodik
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are organic compounds containing double (alkenes) or triple (alkynes) bonds in their molecules.
valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
van der Waals’ force → van der Waalsova sila
Van derWaals’ force is the weak attractive force between two molecules which arises from electric dipole interactions. It can lead to the formation of stable but weakly bound dimer molecules or clusters. They are named after the Dutch physicist Johannes van der Waals (1837-1923).
gasoline → motorni benzin
Gasoline is a complex mixture of volatile hydrocarbons that may have between 5 to 12 carbons. The major components are branched-chain paraffins, cycloparaffins, and aromatics. Gasoline is most often produced by the fractional distillation of crude oil as the fraction of hydrocarbons in petroleum boiling between 30 °C and 200 °C. The quality of a fuel is measured with its octane number. Octane number is the measure of the resistance of gasoline against detonation or preignition of the fuel in the engine. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. The octane number is determined by comparing the characteristics of a gasoline to isooctane with good knocking properties (octane number of 100) and heptane with bad (octane number of 0).
glucose → glukoza
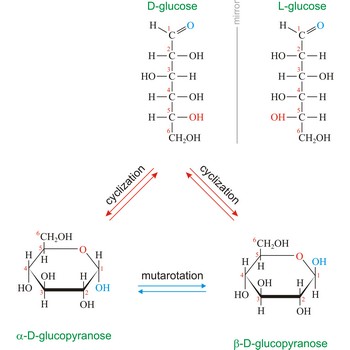
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
vertical ionisation energy → vertikalna energija ionizacije
Vertical ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, molecule, or ion in the gas phase without moving any nuclei. The vertical ionisation energy is greater than or equal to the adiabatic ionisation energy.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Molekula." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table