amount fraction → količinski udio
Amount fraction, xA, (y for gaseous mixtures) is the ratio of the amount of substance (number of moles) of substance A to the total amount of substance in a mixture.
angular momentum → moment količine gibanja
Angular momentum is a physical quantity defined for rotating motion (in analogy to momentum that is defined for linear motion). If a body rotates around a specified axis, its angular momentum equals
Where I is the rotational inertia concerning that axis and ω is the angular velocity of the body.
Angular momentum can also be defined for a point-like body concerning a specified origin (in that case, it is not necessary that the point-like body undergoes circular motion). Rotational inertia of the point-like body, concerning that origin equals:
Where m is the mass of the body and r is its distance from the origin.
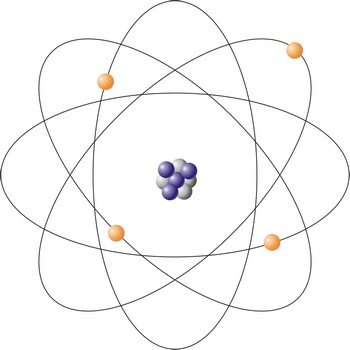
atom → atom
Atom is an atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Rutherford-Bohr’s model represents the atom as a positively charged core of a size around 10-14 m composed of protons (positive particles) and neutrons (neutral particles) around which negatively charged electrons circle. The number of protons and electrons are equal, so the atom is an electrically a neutral particle. Diameter of the atom is about 10-10 m.
fraction → udio
Fraction is a ratio of two quantities of the same kind, the numerator quantity applying to one constituent (or part) of the system and the denominator to the sum of quantities for all constituents (parts) of the system. When applied to mixtures fractions represent a group of three quantities: mass fraction, volume fraction and amount fraction (or mole fraction equal to the number fraction).
gravimetrical factor → gravimetrijski faktor
Gravimetrical factor is stechiometric proportion between molar mass of analyte and molar mass of precipitate in gravimetry.
harmonic motion → harmoničko gibanje
Harmonic motion is caused by restoring force, acting on a body that is displaced from its equilibrium position. This force tries to put the body back in equilibrium. Usual examples are the motion of a body attached to elastic spring (see: Hooke’s law) and the motion of mathematical pendulum. The body undergoes periodic motion around the equilibrium point.
colloid → koloid
Colloids are systems in which there are two or more phases, with one (the dispersed phase) distributed in the other (the continuous phase). Moreover, at least one of the phases has small dimensions, in the range between 1 nm and 1 μm (10-9 m – 10-6 m). Dimension, rather than the nature of the material, is characteristic. In this size range, the surface area of the particle is large with respect to its volume so that unusual phenomena occur, e.g., the particles do not settle out of the suspension by gravity and are small enough to pass through filter membranes. Macromolecules (proteins and other high polymers) are at the lower limit of this range; the upper limit is usually taken to be the point at which the particles can be resolved in an optical microscope.
Colloidal particles may be gaseous, liquid, or solid, and occur in various types of suspensions:
Sols - dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid.
Emulsions - colloidal systems in which the dispersed and continuous phases are both liquids.
Gels - colloids in which both dispersed and continuous phases have a three-dimensional network throughout the material.
Aerosols - colloidal dispersions of liquid or solid particles in a gas.
Foams - dispersions of gases in liquids or solids.
heat of hydration → toplina hidratacije
Heat of hydration or enthalpy of hydration of ions corresponds to the heat that is released by hydration of one mole of ions at a constant pressure. The more the ion is hydrated, the more heat is released. Degree of hydration depends on the size and charge of ion. The smaller the ion and the greater its charge, it will be the more hydrated.
heat of vaporisation → toplina isparavanja
Heat of vaporisation or enthalpy of vaporisation is the heat required to convert a substance from the liquid to the gaseous state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of vaporization).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Molarna veličina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table