activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
agar → agar
Agar, also called agar-agar, is an extract of certain species of red algae (of the Gelidium and Gracilaria genera) that is used as a gelling agent in microbiological culture media, foodstuffs, medicine, and cosmetic. The predominant component of agar is agarose, a polysaccharide made up of subunits of the sugar galactose.
antimony → antimon
Antimony has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word stibium meaning mineral stibnite. It is hard, brittle, silvery-white semimetal. Stable in dry air. Toxic by ingestion or inhalation. Antimony is found in stibnite (Sb2S3) and in valentinite (Sb2O3). It is alloyed with other metals to increase their hardness. Also in the manufacture of a few special types of semiconductor devices. Also in plastics and chemicals. A few kinds of over-the-counter cold and flu remedies use antimony compounds.
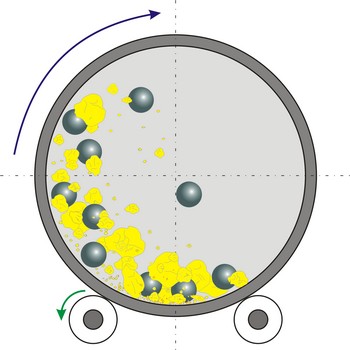
ball mill → kuglični mlin
Ball mill is a grinder for reducing hard materials to powder. The grinding is carried out by the pounding and rolling of a charge of steel or ceramic balls carried within the cylinder. The cylinder rotates at a relatively slow speed, allowing the balls to cascade through the mill base, thus grinding or dispersing the materials.
Type of ball mills, centrifugal and planetary mills, are devices used to rapidly grind materials to colloidal fineness (approximately 1 μm and below) by developing high grinding energy via centrifugal and/or planetary action.
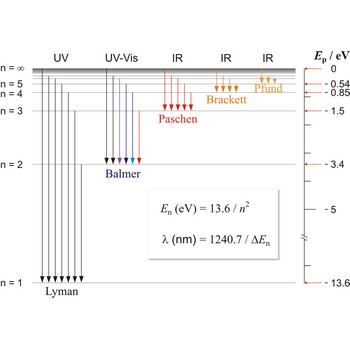
Balmer series → Balmerova serija
Balmer series, Balmer lines is a series of lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen that involve transitions to the n=2 state from states with n>2.
becquerel → bekerel
Becquerel (Bq) is the SI derived unit, with a special name, for radioactivity, equal to s-1. It describes a radioactivity of an amount of radionuclide decaying at the rate, on average, of one spontaneous nuclear transition per second. The unit was named after the French scientist Antoine Henri Becquerel (1852-1908) (disintegrations per unit time), equal to s-1.
chemical glass → kemijsko staklo
Chemical glass is a special, resilient glass used in production of chemical vessels; it is composed of quartz and boron, barium, zinc and aluminium oxides.
chemotherapy → kemoterapija
Chemotherapy is the treatment of disease by means of chemicals that have a specific toxic effect upon the disease producing microorganisms (antibiotics) or that selectively destroy cancerous tissue (anticancer therapy).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Mil-spec." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table