valine → valin
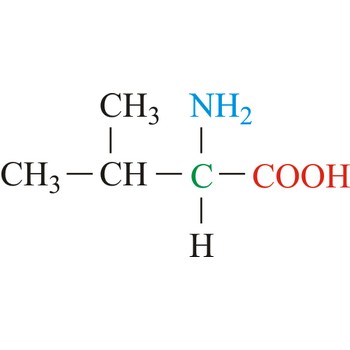
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
van der Waals’ equation → van der Waalsova jednadžba
Van der Waals’ equation is an equation of state for real fluids which takes the form:
where p is pressure, Vm is molar volume, T is temperature, R is the molar gas constant, and a and b are characteristic parameters of the substance which describe the effect of attractive and repulsive intermolecular forces.
van’t Hoff equation → van Hoffova jednadžba
Van’t Hoff equation is the equation expressing the temperature dependence on the equilibrium constant K of a chemical reaction:
where ΔrH° is the standard enthalpy of reaction, R the molar gas constant, and T the temperature.
vanadium → vanadij
Vanadium was discovered by A. M. del Rio (Spain) in 1801 and rediscovered by Nils Sefstrom (Sweden) in 1830. Named after Vanadis, the goddess of beauty in Scandinavian mythology. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resistant to corrosion by moisture, air and most acids and alkalis at room temperature. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. Reacts with concentrated acids. Vanadium is found in the minerals patronite (VS4), vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] and carnotite [K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O]. Pure metal produced by heating with C and Cl to produce VCl3 which is heated with Mg in Ar atmosphere. It is mixed with other metals to make very strong and durable alloys. Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst, dye and fixer-fixer.
visible radiation → vidljivo zračenje
Human eye can only see electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths form 400 nm to 760 nm. This narrow part of electromagnetic spectrum is called visible radiation. Visible (white) light is a mixture of light of all kind of colours, it can be separated, with the help of a glass prism, into its component colours - visible light spectrum, and each colour corresponds to a certain area of wavelengths:
| Colour | Wavelength / nm |
|---|---|
| purple | 400 - 450 |
| blue | 450 - 500 |
| green | 500 - 570 |
| yellow | 570 - 590 |
| orange | 590 - 620 |
| red | 620 - 760 |
velocity → brzina
If a point-like object moves so that its position vector changes from being ri to rf, than the displacement Δr of object is
If a point-like object undergoes a displacement, Δr, in time Δt, its average velocity, v is defined as
The instantaneous velocity, v, is obtained from the average velocity by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average velocity approaches a limiting value, which is the velocity of a given instant:
Velocity is a vector quantity. If we plot the path of a moving particle as a curve in a coordinate system, the instantaneous velocity is always tangent to that curve.
SI unit for velocity is m s-1.
Volta, Alessandro → Volta, Alessandro
The Italian physicist Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (1745-1827) was the inventor of the voltaic pile, the first electric battery (1800). In 1775 he invented the electrophorus, a device that, once electrically charged by having been rubbed, could transfer charge to other objects. Between 1776 and 1778, Volta discovered and isolated methane gas (CH4). The electrical unit known as the volt was named in his honor.
volumetric flask → odmjerna tikvica
Volumetric flasks are bottles made of glass, in a pear like in shape with long thin necks and flat bottoms. All come with a ground glass stopper for a tight seal. Volume marking is cut in glass with fluoride acid around the neck, so that parallax should be avoided (flask is put in front of the eyes so that one can see only a straight horizontal line). A volumetric flask is calibrated to contain (TC or In) the indicated volume of water at 20 °C when the bottom of the meniscus is adjusted to just rest on the center of the line marked on the neck of the flask. They are used for preparing the exactly known volume of sample solution and standard solutions of reagents. On each flask with volume designation a temperature on which the flask has been calibrated is designated.
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
wash bottle → boca štrcaljka
Plastic wash bottle is a squeeze bottle made of low density polyethylene (LDPE) whose contents can be forced out through a narrow hole at the top by squeezing the bottle.
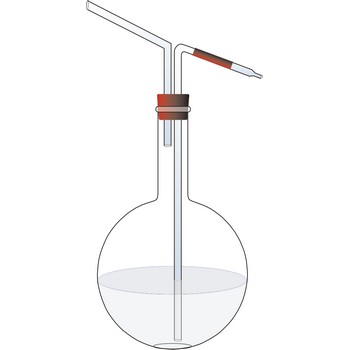
Glass wash bottle is a bottle fitted with two glass tubes pass through the cap, so that on blowing into one of the tubes a stream of water issuing from the other may be directed upon anything to be washed or rinsed, as a precipitate upon a filter.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table