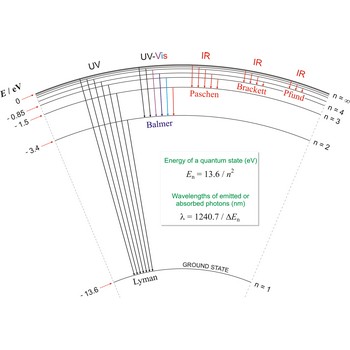
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
weber → veber
Weber (Wb) is the SI derived unit of magnetic flux. The weber is the magnetic flux which, linking a circuit of one turn, produces in it an electromotive force of one volt as it is reduced to zero at a uniform rate in one second (Wb = V·s). The unit was named after the German scientist W.E. Weber (1804-1891).
white spirit → bijeli špirit
White spirit (mineral spirits, petroleum spirits) is a paraffin-derived clear, transparent liquid which is a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating.
X-ray spectrum → spektar X-zraka
X-ray spectrum is a set of characteristic X-ray frequencies or wavelengths produced by a substance used as a target in an X-ray tube. Each element has a characteristic X-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number and the frequencies of certain lines in the X-ray spectrum.
macromolecule → makromolekule
Macromolecule is a molecule of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetitions of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. The types of macromolecules are natural and synthetic polymers, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins etc. Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is made up of hundreds, even thousands of glucose molecules strung together.
magnesium → magnezij
Magnesium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Magnesia, a district of Thessaly. It is lightweight, malleable, silvery-white metal. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame and reacts with water as temperature elevates. Can ignite in air. React violently with oxidants. Magnesium is found in large deposits in the form of magnesite, dolomite and other minerals. It is usually obtained by electrolysis of melted magnesium chloride (MgCl2) derived from brines, wells and sea water. Used in alloys to make airplanes, missiles and other uses for light metals. Have structural properties similar to aluminium.
magnetic permeability → magnetska permeabilnost
Magnetic permeability (μ), also called permeability, is a constant of proportionality that exists between magnetic induction and magnetic field intensity. This constant is equal to approximately μo = 1.257×10-6 H/m in a vacuum.
Magnetic permeability is often expressed in relative, rather than in absolute, terms. If μ represents the permeability of the substance in question, then the relative permeability, μr, is given by:
manganese → mangan
Manganese was discovered by Johann Gahn (Sweden) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word magnes meaning magnet, or magnesia nigri meaning black magnesia (MnO2). It is hard, brittle, grey-white metal with a pinkish tinge. Impure forms are reactive. Rusts like iron in moist air. Manganese is most abundant ores are pyrolusite (MnO2), psilomelane [(Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10] and rhodochrosite (MnCO3). Pure metal produced by mixing MnO2 with powered Al and ignited in a furnace. Used in steel, batteries and ceramics. The steel in railroad tracks can contain as much as 1.2 % manganese. It is crucial to the effectiveness of vitamin B1.
mass fraction → maseni udio
Mass fraction (wA) is the ratio of the mass of substance A to the total mass of a mixture.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table