neon → neon
Neon was discovered by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word neon meaning new. It is colourless, odourless inert gas. Non-reactive even with fluorine. Fourth most abundant element in the universe. Neon is obtained by liquefaction of air and separated from the other gases by fractional distillation. Primarily for lighting.
Nessler’s reagent → Nesslerov reagens
Nessler’s reagent is a solution of mercury(II) iodide (HgI2) in potassium iodide and potassium hydroxide named after the German chemist Julius Nessler (1827-1905). It is used in testing for ammonia, with which it forms a brown coloration or precipitate.
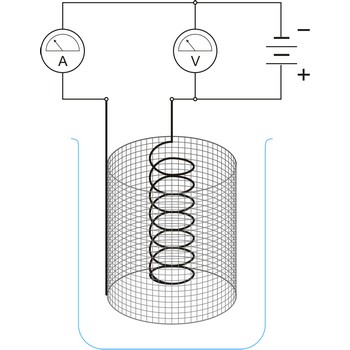
electrogravimetry → electrogravimetrija
Electrogravimetry is an electroanalytical technique in which the substance to be determined (usually a metal) is deposited out on an electrode which is weighed before and after the experiment. The potential of the electrode must be carefully chosen to ensure that only the metal do be determined will deposit.
electrolytes → elektroliti
Electrolytes are substances which, when melted or dissolved in water, conduct electric current. By melting or dissolving they are dissociated into electrically charged particles (ions) which are able to conduct electric current. By passing of electric current the transfer of matter occurs. Positively charged particles (cations) travel towards the negative pole (the cathode) and negatively charged particles (the anions) travel towards the positive pole (the anode). Liquid metals, in which the conduction is by free electrons, are not usually regarded as electrolytes. Solid conductors of ions, as in the sodium-sulphur cell, are also known as electrolytes. Depending upon how it conducts electric current, matter can be divided into strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes and nonconductors.
electron configuration → elektronska konfiguracija
The electron configuration shows how many electrons there are in an atom or ion and their distribution along orbitals (see Table of electronic configuration of elements). Structure and all regularity in the periodic system depend upon electronic configuration of atoms of elements. Characteristics of elements mainly depend on electronic configuration of the outer shell. Refilling of the new electronic shell atoms of elements of similar electronic configuration emerge as well as in the previous shell, which adds up to periodicities of characteristics of elements.
electrophoresis → elektroforeza
Electrophoresis is a technique for the analysis and separation of colloids, based on the movement of charged colloidal particles in an electric field. The migration is toward electrodes of charge opposite to that of the particles. The rate of migration of the particles depends on the field, the charge on the particles, and on other factors, such as the size and shape of the particles.
Electrophoresis is important in the study of proteins. The acidity of the solution can be used to control the direction in which a protein moves upon electrophoresis.
nominal → nominalno
Nominal is used to describe a process where 100 % accuracy is not guaranteed. For example, sand filtres are usually sold to filtre to a nominal 10 μm, which means that they will filtre most particles of 10 μm and larger, but not all. A filtre which is guaranteed to filtre all particles of 10 μm would be termed absolute rather than nominal.
electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table