Helmholz free energy → Helmholzova slobodna energija
Helmholz free energy (A) is a thermodynamic function defined by A = U - TS, where U is the internal energy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. For a reversible isothermal process ΔA represents the useful work available.
colloid ion → koloidni ion
Colloid ions emerge when colloid particles adsorb certain type of ion from solution and thus become charged with the same charge. The charge can also originate form a chemical reaction of colloid particle’s surface. Colloid ions formed by absorption of silver chloride particle can be show as follows:
Adsorbed layer is monomolecular (one molecule thick) and which type of ion will be formed depends upon which ions are present in a greater number in the solution in. Because of this colloid particles are charged with the same charge, mutual repelling occurs, and the colloid solution becomes stable. Colloid charge can be determined by electrophoresis.
colloid mill → koloidni mlin
Colloid mills are machines used to grind aggregates into very fine particles or to apply very high shearing within a fluid to produce colloid suspensions or emulsions in which the particle sizes are less than 1 micrometer. One type of colloid mill is called a disc mill, in which a mixture of a solid and liquid (or two liquids) is passed between two discs a small distance apart, which rotate very rapidly relative to each other. Applications of colloid mills occur in food processing, in paint manufacture, and in the pharmaceutical industry.
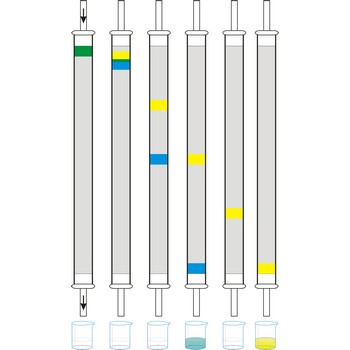
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
combustible → zapaljiv
The term combustible is often used to describe any material which will burn. However, conditions at which combustion will occur must be defined more accurately, for example a combustible liquid is 37.8 °C but below 93.3 °C. This allows a distinction to be made between combustible materials, which are fairly difficult to ignite, and flammable or highly flammable ones, which are far easier to ignite.
heterocyclic compounds → heterociklički spojevi
Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds having as ring members atoms of at least two different elements, e.g., quinoline, 1,2-thiazole.
high-density polyethylene → polietilen visoke gustoće
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polyolefin with a density of from 0.941 g/cm3 to 0.960 g/cm3. It is a recyclable plastic, used for items such as milk containers, detergent containers, and base cups of plastic soft drink bottles. HDPE has a high degree of resistance to chemicals, is easy to keep clean, and easily welded.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table