fire-damp → plin praskavac
Fire-damp is a mixture of two volume parts of hydrogen and one volume part of oxygen which, if set on fire, strongly explodes, the flame giving of a very high temperature (2 000 °C).
flash point → temperatura zapaljenja
Flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid or volatile solid gives off vapour sufficient to form an ignitable mixture with the air near the surface of the liquid or within the test vessel (NFPA).
flashback → uskakanje plamena
Flashback occurs when the flame in a gas torch burns back into the torch or hose; this is often accompanied by a hissing or squealing sound, and a pointed or smoky flame.
cement → cement
Cement is any various substances used for bonding or setting to a hard material. Portland cement is a mixture of calcium silicates and aluminates made by heating limestone (CaCO3) with clay (containing aluminosilicates) in a kiln. The product is ground to a fine powder. When mixed with water it settles in a few hours and then hardens over a longer period of time due to the formation of hydrated aluminates and silicates.
centrifugation → centrifugiranje
Centrifugation is sedimentation of particles under the influence of the centrifugal force and it is used for separation of superfine suspensions. At centrifuging forces up to 10 000 times greater than gravity force are used, and at ultracentrifuge up to 600 000 times as great.
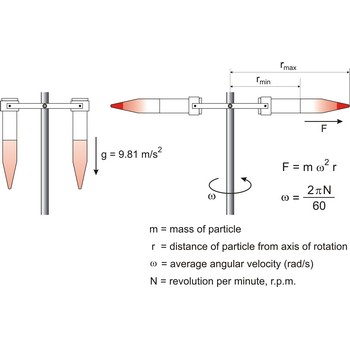
centrifuge → centrifuga
Centrifuge is a device in which solid or liquid particles of different densities are separated by rotating them in a tube in a horizontal circle. The dense particles tend to move along the length of the tube to a greater radius of rotation, displacing the lighter particles to the other end.
cerium → cerij
Cerium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) and by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1803 and Wilhelm von Hisinger (Germany) in 1814. Named after the asteroid Ceres this discovered two years before the element. It is malleable, ductile, iron-grey metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts easily with water. Dissolves in acids; ignites when heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Strong reductant. Cerium is most abundant rare earth metal. Found in many minerals like monazite sand [Ce(PO4)]. Its oxides are used in the optics and glass-making industries. Its salts are used in the photography and textile industry. Used in high-intensity carbon lamps and as alloying agents in special metals.
fluid mechanics → mehanika fluida
Fluid mechanics is the study of various properties of the fluid (liquids and gases): velocity, pressure, density and temperature, as functions of space and time.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table