propagation → propagacija
Propagation is the step in a polymerization mechanism, where new monomer molecules are added to the growing polymer chain in the free radical process.
protein → bjelančevina
Proteins are natural organic compounds of animal or herbal origin, essential in diet. They are natural polymers developed from a crowd of interconnecting monomers of amino acids, with relative molecular masses amounting up to a few million.
fructose → fruktoza
Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketonic sugar), which occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, C6H12O6, but have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is a very sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. An older common name for fructose is levulose, after its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left (in contrast to glucose which is dextrorotatory). The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose.
halocarbon → halogenirani ugljikovodik
Halocarbon is a compound containing no elements other than carbon, one or more halogens, and sometimes hydrogen. The simplest are compounds such as tetrachloromethane (CCl4), tetrabromomethane (CBr4), etc. The lower members of the various homologous series are used as refrigerants, propellant gases, fireextinguishing agents, and blowing agents for urethane foams. When polymerized, they yield plastics characterized by extreme chemical resistance, high electrical resistivity, and good heat resistance.
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
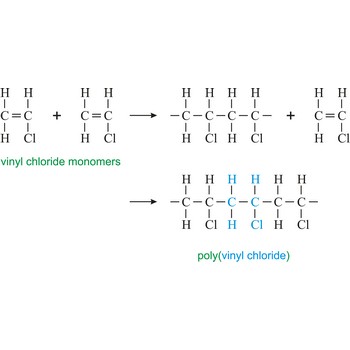
polyvinyl chloride → polivinil klorid
Poly(vinyl chloride) or the PVC is hard and resistant homopolymer produced by the polymerization of the gas vinyl chloride [CH2CHCl]. The pure polymer is hard, brittle and difficult to process, but it becomes flexible when plasticizers are added. After mixing with plasticizers, stabilizers, and pigments, the resin may be fabricated by techniques such as calendering, molding, or extrusion into flexible articles such as raincoats, shower curtains, and packaging films. The resin is not plasticized for use in making rigid products such as water pipe, plumbing fittings, and phonograph records.
styrene → stiren
Styrene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon (C6H5OC2H3O) colourless, toxic liquid with a strong aromatic aroma. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and carbon disulfide, but dissolves only slightly in water. It is used to make plastics such as polystyrene, ABS, styrene-butadiene rubber styrene-butadiene latex and unsaturated polyesters.
Wagner tube → Wagnerova cijev
Wagner tube or drop catcher impedes the movement of distillate drops from the distillation flask to the condensing chamber.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kondenzacijska polimerizacija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table