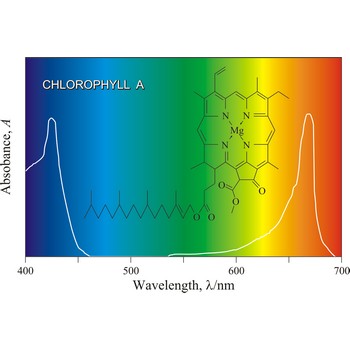
chlorophyll → klorofil
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in green plants and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll is essential in the transformation of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light mostly in the blue and red ends of the visible spectrum, and very little in the green wavelengths. That green light is reflected, giving us the leaf colour we see.
Clapeyron equation → Clapeyronova jednadžba
Clapeyron equation (also called the Clausius-Clapeyron equation) is a relation between pressure and temperature of two phases of a pure substance that are in equilibrium,
where ΔtrsS is the difference in entropy between the phases and ΔtrsV the corresponding difference in volume.
free energy → slobodna energija
Free energy is an energy that is actually available to do useful work. A decrease in free energy accompanies any spontaneous process. Free energy does not change for systems that are at equilibrium.
geochemistry → geokemija
Geochemistry is the scientific study of the chemical composition of the Earth. It includes the study of the abundance of the Earth’s elements and their isotopes and the distribution of the elements in environments of the Earth (lithosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere).
Grignard reagent → Grignardov reagens
Grignard reagents are organomagnesium halides, RMgX, having a carbon- magnesium bond (or their equilibrium mixtures in solution with R2Mg + MgX2).
harmonic motion → harmoničko gibanje
Harmonic motion is caused by restoring force, acting on a body that is displaced from its equilibrium position. This force tries to put the body back in equilibrium. Usual examples are the motion of a body attached to elastic spring (see: Hooke’s law) and the motion of mathematical pendulum. The body undergoes periodic motion around the equilibrium point.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
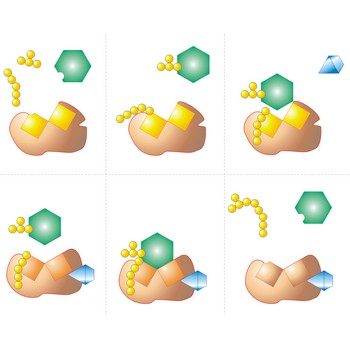
colloid ion → koloidni ion
Colloid ions emerge when colloid particles adsorb certain type of ion from solution and thus become charged with the same charge. The charge can also originate form a chemical reaction of colloid particle’s surface. Colloid ions formed by absorption of silver chloride particle can be show as follows:
Adsorbed layer is monomolecular (one molecule thick) and which type of ion will be formed depends upon which ions are present in a greater number in the solution in. Because of this colloid particles are charged with the same charge, mutual repelling occurs, and the colloid solution becomes stable. Colloid charge can be determined by electrophoresis.
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska ravnoteža." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table