Curie → Curie
Maria Sklodowska-Curie (1867-1934) Polish-born French chemist who went to Paris in 1891. She married the physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906) in 1985 and soon began work on seeking radioactive elements other than uranium in pitchblende (to account for its unexpectedly high radioactivity). By 1898 she had discovered radium and polonium although it took her years to purify them. In 1903 the Curies shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Henri Becquerel, who had discovered radioactivity.
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
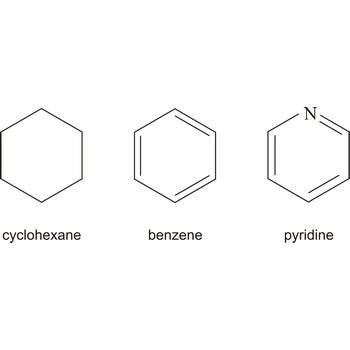
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
kinetic theory → kinetička teorija
Kinetic theory explains the behaviour of solids, liquids and gases and their state changes dependable upon motion of particles they are made of.
Dalton’s atomic theory → Daltonova atomska teorija
Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory of chemical combination, first stated by John Dalton in 1803. It involves the following postulates:
1. Elements consist of indivisible small particles (atoms).
2. All atoms of the same element are identical; different elements have different types of atom.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
4. ’Compound elements’ (i.e. compounds) are formed when atoms of different elements join in simple ratios to form ’compound atoms’ (i.e. molecules).
Dalton also proposed symbols for atoms of different elements (later replaced by the present notation using letters).
density → gustoća
In the most common usage, density (ρ) is mass density or mass per unit volume. In Si units it is measured in kg m-3. More commonly, densities are given in kg dm-3.
More generally, it is the amount of some quantity (mass, charge, energy, etc.) divided by a length, area, or volume.
Relative density is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some reference substance. For liquids or solids, it is the ratio of the density (usually at 20 °C) to the density of water at 4 °C. This quantity was formerly called specific gravity.
diastereoisomer → dijastereoizomer
Diastereoisomers (diastereomers) are stereoisomers of a compound having two or more chiral centers that are not a mirror image of another stereoisomer of the same compound. For example, in the structure below, 1 and 2 are enantiomers and so are 3 and 4; 1 and 3 are diastereoisomers, as are 2 and 4. Unlike enantiomers, diastereoisomers need not have closely similar physical and chemical properties
law of definite composition → zakon o određenom sastavu
Law of definite composition states that the elements in a given compound are always combined in the same proportion by mass. This law form the basis for the definition of a chemical compound.
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Lewis base → Lewisova baza
Lewis base is an agent capable of donating a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
limiting reactant → mjerodavni reaktant
Limiting reactant is a reactant in a chemical reaction that limits the amount of product that can be formed. The reaction will stop when the entire limiting reagent is consumed. These other reactants are present in excess.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska promjena." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table