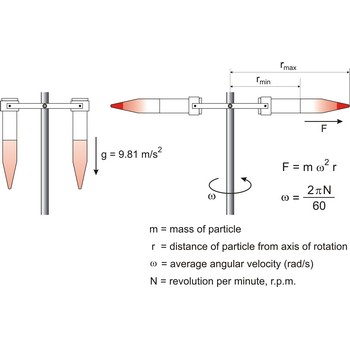
centrifuge → centrifuga
Centrifuge is a device in which solid or liquid particles of different densities are separated by rotating them in a tube in a horizontal circle. The dense particles tend to move along the length of the tube to a greater radius of rotation, displacing the lighter particles to the other end.
decomposing → raščinjavanje
Decomposing in analytical chemistry means that a certain substance is converted, by melting it with a suitable melting medium (sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, ...) in the kind of compound which will afterwards that dissolve in water, acid or base very easily.
degenerate orbitals → degenerirane orbitale
Degenerate orbitals are orbitals with the same energy. This degeneracy can sometimes be "lifted" by external electric or magnetic fields.
dehydrogenation → dehidrogenacija
Dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen is removed from a compound. Dehydrogenation of organic compounds converts single carbon-carbon bonds into double bonds. It is usually affected by means of a metal catalyst or in biological systems by enzyme dehydrogenases.
change of state → promjena stanja
Change of state is a physical change which appears when a substance crosses from one state into another. This usually happens because of the change of energy of particles provoked by heating or cooling.
detergent → deterdžent
Detergent is a substance added to water to improve its cleaning properties. Although water is a powerful solvent for many compounds, it will not dissolve grease and natural oils. Detergents are compounds that cause such nonpolar substances to go into solution in water. Soap is the original example, owing its action to the presence of ions formed from long-chain fatty acids ion (e.g. stearat ion, CH3(CH2)16COO-).
effervescence → pjenušanje
Effervescence is the formation of gas bubbles in a liquid by a chemical reaction. An example of effervescence is the release of carbon dioxide which bubbles as a gas from the liquid when limestone chips, which are composed of calcium carbonate, are added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
electron pair → elektronski par
Electron pair is two electrons within one orbital with opposite spins responsible for a chemical bond.
electron spin → elektronski spin
Electron spin (s) is the quantum number, equal to 1/2, that specifies the intrinsic angular momentum of the electron.
electron volt → elektronvolt
Electron volt (eV) is a non-SI unit of energy used in atomic and nuclear physics, equal to approximately 1.602 177×10-19 J. The electron volt is defined as the kinetic energy acquired by an electron upon acceleration through a potential difference of 1 V.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska energija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table