blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
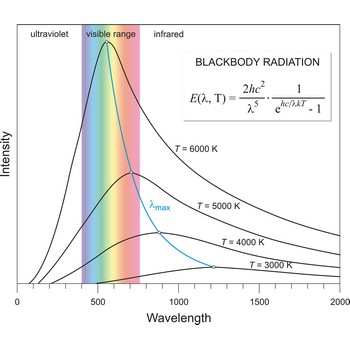
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
butane → butan
Butane is a gaseous hydrocarbon C4H10 obtained from petroleum (refinery gas or by cracking higher hydrocarbons). The fourth member of the alkane series, it has a straight chain of carbon atoms and is isomeric with 2-methylpropane, formerly called isobutene. It can easily be liquefied under pressure and is supplied into cylinders for use as a fuel gas. It is also a raw material for making buta-1, 3-diene for synthetic rubber.
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
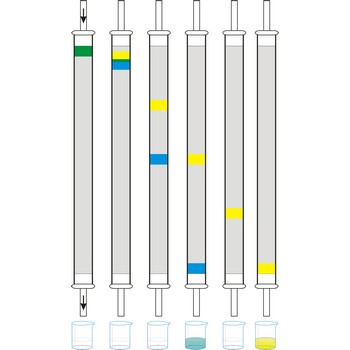
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
critical temperature → kritična temperatura
Critical temperature is the temperature of the liquid-vapour critical point, that is, the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by an increase of pressure.
cryogenic fractionation → kriogena frakcinacija
Cryogenic fractionation is a process of separation of gases by cooling them until they enter their liquid state. Large scale gas production companies use this method to produce liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen etc. Gases have different boiling points (the temperature at which they change from liquid to gas). Oxygen has a boiling point of -183 °C, and nitrogen a boiling point of -195.8 °C. Therefore by cooling the gas mixture to -183 °C, the oxygen can be collected as liquid and the nitrogen remains its gaseous form.
heat of sublimation → toplina sublimacije
Heat of sublimation or enthalpy of sublimation is the energy required to convert one mole of a substance from the solid to the gas state (sublimation) without the appearance of the liquid state.
heat of vaporisation → toplina isparavanja
Heat of vaporisation or enthalpy of vaporisation is the heat required to convert a substance from the liquid to the gaseous state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of vaporization).
irreversible process → ireverzibilni proces
If a system is taken from one state to another but cannot be brought back to the same initial state, then the process is called irreversible. Some examples are free expansion of a gas; dissipation of energy due to friction, or the mixing of two gases or liquids etc.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednadžba stanja idealnog plina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table