cubic close-packed structure → kubična gusta slagalina
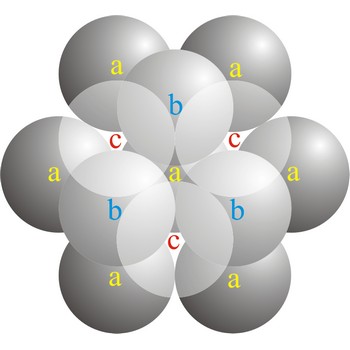
In a cubic close-packed (ccp) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of four layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers (a) contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The atoms in the second layer (b) fit into depressions in the first layer. The atoms in the third layer (c) occupy a different set of depressions than those in the first. The cubic close packed structure can be made by piling layers in the a-b-c-a-b-c-a-b-c... sequence.
crystal system → kristalni sustav
Crystal system is a method of classifying crystalline substances on the basis of their unit cell. There are seven unique crystal systems. The simplest and most symmetric, the cubic (or isometric) system, has the symmetry of a cube. The other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic.
|
Crystal system
|
Unit-cell
|
Conditions on unit-cell edges and angles |
|
cubic |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
|
hexagonal |
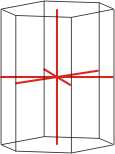 |
a≠c α=γ=90° β=120° |
|
tetragonal |
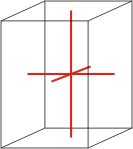 |
a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
rhombohedral |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
|
orthorhombic |
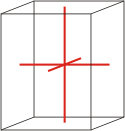 |
a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
monoclinic |
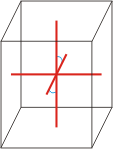 |
a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
|
triclinic |
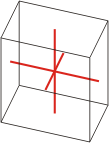 |
a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
face-centered cubic lattice → plošno centrirana kubična rešetka
Face-centered cubic lattice (fcc or cubic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a =b =c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the fcc structures the spheres fill 74 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is four (8×1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4). There are 26 metals that have the fcc lattice.
face-centered orthorhombic lattice → plošno centrirana ortorompska rešetka
Face-centered orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
hexagonal close-packed structure → heksagonska gusta slagalina
In a hexagonal close-packed (hcp) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of three layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers (a) contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The middle layer (b) contains three atoms nestled between the atoms of the top and bottom layers, hence, the name close-packed. The hexagonal close packed structure can be made by piling layers in the a-b-a-b-a-b... sequence.
hexagonal lattice → heksagonska rešetka
Hexagonal lattice has lattice points at the twelve corners of the hexagonal prism and at the centers of the two hexagonal faces of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=90° and γ=120°.
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
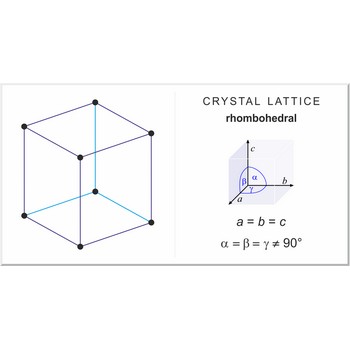
rhombohedral lattice → romboedarska rešetka
Rhombohedral (or trigonal) lattice has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b=c and interaxial angles α=β=γ≠90°.
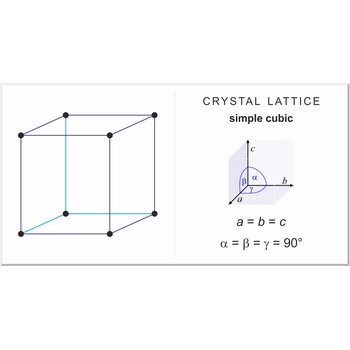
simple cubic lattice → jednostavna kubična rešetka
Simple or primitive cubic lattice (sc or cubic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angels α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the sc structures the spheres fill 52 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is one (8×1/8 = 1). This is only one metal (α-polonium) that have the sc lattice.
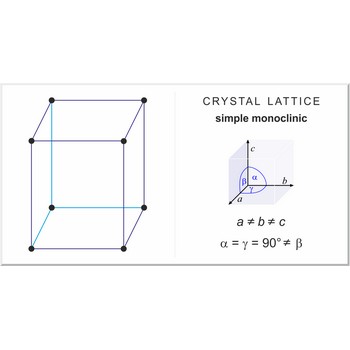
simple monoclinic lattice → jednostavna monoklinska rešetka
Simple or primitive monoclinic lattice (monoclinic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=γ=90°≠β.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jedinična ćelija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table