alkanes → alkani
Alkanes (paraffins) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2, and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkane names end in the suffix -ane. They form a homologous series (the alkane series) methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), etc. The lower members of the series are gases; the high-molecular mass alkanes are waxy solid. Generaly the alkanes are fairly unreactive. They form haloalkanes with halogens when irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. Alkanes are present in natural gas and petroleum.
amount fraction → količinski udio
Amount fraction, xA, (y for gaseous mixtures) is the ratio of the amount of substance (number of moles) of substance A to the total amount of substance in a mixture.
argon → argon
Argon was discovered by Lord Raleigh and Sir William Ramsay (Scotland) in 1894. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word argos meaning inactive. It is colourless and odourless noble gas. Chemically inert. It is the third most abundant element in the earth’s atmosphere and makes up about 1 %. Argon is continuously released into the air by decay of radioactive potassium-40. Pure form is obtained from fractional distillation of liquid air. Used in lighting products. It is often used in filling incandescent light bulbs. Some is mixed with krypton in fluorescent lamps. Crystals in the semiconductor industry are grown in argon atmospheres.
blackbody → crno tijelo
In radiation physics, an ideal blackbody is a theoretical object that absorbs all the radiant energy falling upon it and emits it in the form of thermal radiation. Planck’s radiation law gives the power radiated by a unit area of blackbody, and the Stefan-Boltzman law expresses the total power radiated.
butane → butan
Butane is a gaseous hydrocarbon C4H10 obtained from petroleum (refinery gas or by cracking higher hydrocarbons). The fourth member of the alkane series, it has a straight chain of carbon atoms and is isomeric with 2-methylpropane, formerly called isobutene. It can easily be liquefied under pressure and is supplied into cylinders for use as a fuel gas. It is also a raw material for making buta-1, 3-diene for synthetic rubber.
chemical raw material → kemijske sirovine
Chemical raw material are petroleum fractions used for obtaining organic chemicals, those are mostly refined gas and petroleum or fraction parts of petrol.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
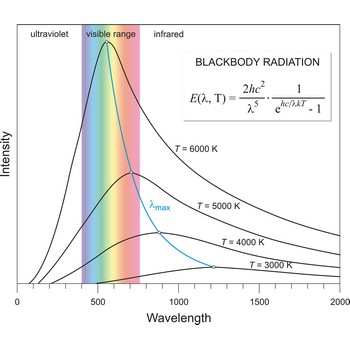
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
Boltzmann constant → Boltzmannova konstanta
The Boltzmann constant (k or kB) is the physical constant describing the relationship between the thermodynamic temperature and the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas. It equals the molar gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA and has the value 1.380 648 52(79)×10-23 J/K. It is named after the Austrian physicist Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Idealni plin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table