Einstein, Albert → Einstein, Albert
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) is a German born American physicist, who took Swiss nationality in 1901. A year later he went to work in the Bern patent office. In 1905. he published five enormously influential papers, one on Brownian movement, one on the photoelectric effect, one on the special theory of relativity, and one on energy and inertia (which included the famous expression E = mc2). In 1915 he published the general theory of relativity, concerned mainly with gravitation. In 1921 he was awarded the Nobel Prize. In 1933, as a Jew, Einstein decided to remain in the USA (where he was lecturing), as Hitler had come to power. For the remainder of his life he sought a unified field theory. In 1939 he informed president Roosevelt that an atom bomb was feasible and that. Germany might be able to make one.
synthetic material → sintetički materijal
Synthetic material (artificial material) is a substance manufactured by chemical synthesis.
thermal conductivity → toplinska vodljivost
Thermal conductivity (Λ) is rate of heat flow divided by the area and by the temperature gradient.
electrodeposition → elektrodepozicija
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing solid materials on an electrode surface using electrolysis. It is a somewhat loosely used term that is applied to many technologies. There are a number of metal deposition technologies. However, not only metals but also different compounds can be electrodeposited. This is used most often for the formation of oxides (such as manganese dioxide and lead dioxide) by anodic oxidation of dissolved salts.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
epimer → epimer
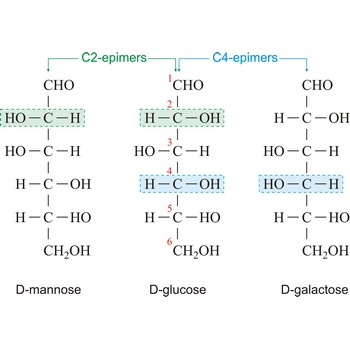
Epimers are diastereoisomers that have the opposite configuration at only one of two or more chiral centers present in the respective molecular entities. For example D-glucose and D-mannose, which differ only in the stereochemistry at C-2, are epimers, as are D-glucose and D-galactose (which differ at C-4).
filtration → filtriranje
Filtration is a procedure in which liquids are separated from the precipitate by passing a suspension through the filter. The precipitate remains on the filter and through it the filtrate passes. Gaseous heterogeneous mixtures can also be filtrated.
thermoplastic → termoplastika
Thermoplastic is ap lastic polymer material that can be repeatedly softened through heating and hardened again by cooling. Examples are PVCor polistiren, which when heated, softens to enable moulding and welding, but on cooling hardens. If the finished product is not correct, the material can be heated and manipulated again.
transference number → prijenosni broj
Transference number of an ion is the fraction of the total current that is carried by that ion during electrolysis. Different ions carry different fractions of the current because different ions move at different speeds under the same potential gradient. In general, a cation and an anion differ in the amount of current they can carry during electrolysis.
ultracentrifuge → ultracentrifuga
Ultracentrifuge is a high-speed centrifuge used in the separation of colloidal or submicroscopic particles. The ultracentrifuge can generate forces thousands or millions of times stronger than the force of gravity.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "How many oz in a gram." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table