acceleration → akceleracija
If a point-like object undergoes a change in velocity Δv=vf-vi in time Δt=tf-ti (indexes i and f stand for initial and final instant as well as for initial and final velocity) its average acceleration, a is defined as
The instantaneous acceleration, a, is obtained from the average acceleration by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average acceleration approaches a limiting value, which is the acceleration of a given instant:
Acceleration is a vector quantity. SI unit for acceleration is m s-2.
accelerator → akcelerator
Accelerator is a device (machine) used for acceleration of charged particles (protons, deuterons, α-particles). Particles are accelerated under the influence of an electric field and with the help of a magnetic field are kept inside a certain space. When the particles reach enough acceleration (that is sufficient energy), they are directed on a target we wish to bomb. Best known types cyclotron, synchrotron, betatron.
Accelerator is a substance that increases the rate of chemical reaction, i.e. a catalyst.
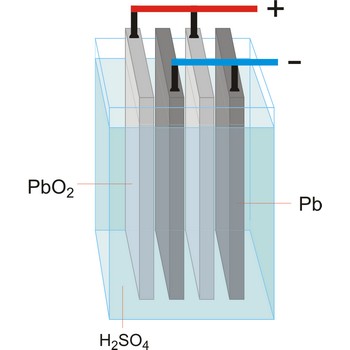
accumulator → akumulator
Accumulator (secondary cell, storage battery) is a type of voltaic cell or battery that can be recharged by passing current through it from an external D.C. supply. The charging current reverses the chemical reactions in the cell. The common types are the lead-acid accumulator and the nickel-cadmium cell.
adiabatic process → adijabatski proces
Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat enters or leaves the system. In general, an adiabatic change involves a fall or rise in temperature of the system.
aldehydes → aldehidi
Aldehydes are a broad class of organic compounds having the generic formula RCHO, and characterized by an unsaturated carbonyl group (C=O). They are formed from alcohols by either dehydrogenation or oxidation. Their chemical derivation is indicated by the name al(cohol) + dehyd(rogenation). An example of these distinct aromatic compounds is formaldehyde.
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
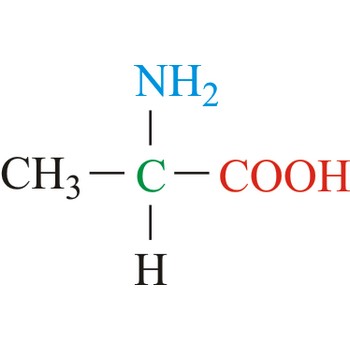
alanine → alanin
Alanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is the second simplest amino acid, but used the most in proteins. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be manufactured by the human body, and does not need to be obtained directly through the diet.
- Abbreviations: Ala, A
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2
- Molecular weight: 89.09 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hera chan tvb." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table