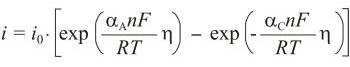fluid mechanics → mehanika fluida
Fluid mechanics is the study of various properties of the fluid (liquids and gases): velocity, pressure, density and temperature, as functions of space and time.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
convection → konvekcija
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from one part of a fluid to another by movement of the fluid itself. There are two methods by which this can be carried out.
Natural convection, in which movement occurs as a result of gravity. Heat transferred through a fluid medium, such as air or water, by currents that result from the rising of less dense, warm fluid and the sinking of heavier, cooler fluid.
Forced convection is where hot fluid is transferred from one region to another by a mechanical means (fans or pumps).
diatomaceous earth → dijatomejska zemlja
Diatomaceous earth is a naturally occurring siliceous sedimentary mineral compound from microscopic skeletal remains (frustules) of diatoms, unicellular aquatic plants of microscopic size. Their fossilized remains are called diatomite and contains approximately 3000 diatom frustules per cubic millimetre.
Diatomite is relatively inert and has a high absorptive capacity, large surface area, and low bulk density. It consists of approximately 90 % silica, and the remainder consists of compounds such as aluminum and iron oxides. The fine pores in the diatom frustules make diatomite an excellent filtering material for waters, beverages, oils, chemicals, as well as many other products.
intensive property → intenzivno svojstvo
intensive property is a property that does not change when the amount of sample changes. Examples are density, pressure, temperature, colour.
lactodensimeter → laktodenzimetar
Lactodensimeter is a special aerometer used for determining the density of milk.
dipole → dipol
Dipole is a pair of separated opposite electric charges. Electric dipole is an assemblage of atoms or subatomic particles having equal electric charges of opposite sign separated by a finite distance. In the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Gustoća." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table