Bronsted base → Bronstedova baza
Brønsted base is a material that accepts hydrogen ions in a chemical reaction.
activation energy → energija aktivacije
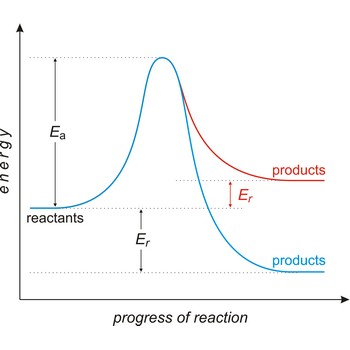
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
active site → aktivno mjesto
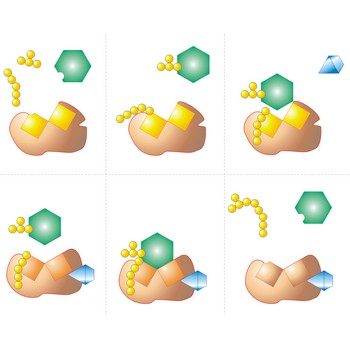
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
calorimetry → kalorimetrija
Calorimetry is a measurement of the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction, change of state, or formation of a solution, or any other event that includes heat transfer.
carboxylate ion → karboksilatni ion
Carboxylate ion is gained when carboxylic acid reacts with water.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
chemical compound → kemijski spoj
Some substance is a compound only if it can be decomposed into two or more different substances by means of a chemical reaction. If two or more substances react, thus creating a new substance, that new substance is called a chemical compound.
chemical element → kemijski element
Chemical element is a type of matter of which elementary matter is composed. Chemical element is composed of atoms with the same core charge.
chemical energy → kemijska energija
Chemical energy is the energy stored in substances and transferred during chemical reaction.
chemical equation equalization → izjednačavanje kemijske jednadžbe
Chemical equation equalization is determining values of stechiometric coefficients of reactants and products in a chemical equation in a way that the number of atoms of each element is equal before and after the reaction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elementarna reakcija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table