thermodynamics → termodinamika
Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other forms of energy.
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
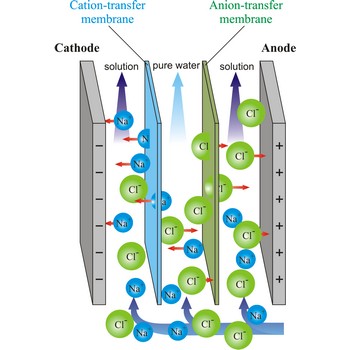
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
transference number → prijenosni broj
Transference number of an ion is the fraction of the total current that is carried by that ion during electrolysis. Different ions carry different fractions of the current because different ions move at different speeds under the same potential gradient. In general, a cation and an anion differ in the amount of current they can carry during electrolysis.
electrolysis → elektroliza
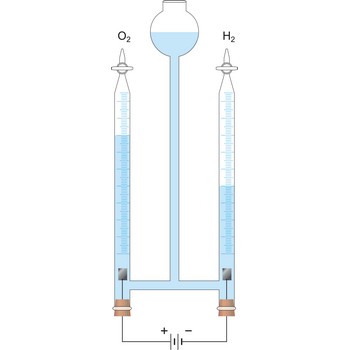
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a substance as a result of passing an electric current between two electrodes immersed in the sample.
electrophoresis → elektroforeza
Electrophoresis is a technique for the analysis and separation of colloids, based on the movement of charged colloidal particles in an electric field. The migration is toward electrodes of charge opposite to that of the particles. The rate of migration of the particles depends on the field, the charge on the particles, and on other factors, such as the size and shape of the particles.
Electrophoresis is important in the study of proteins. The acidity of the solution can be used to control the direction in which a protein moves upon electrophoresis.
voltametry → voltametrija
Voltametry is a common name for a large group of instrumental techniques which are based on measuring the electric current formed by a continuous potential shifting on the electrodes.
electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
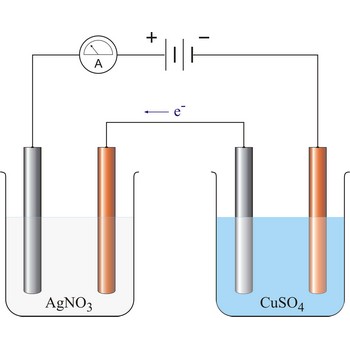
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
ferrite → ferit
Ferrites are ceramic materials of the nominal formula MO·Fe2O3, where M is a divalent metal (Co, Mn, NI, or Zn). The ferrites show either ferrimagnetism or ferromagnetism, but are not electrical conductors, and they are used in high-frequency circuits as magnetic cores, in rectifiers on memory and record tapes, and various related uses in radio, television, radar, computers, and automatic control systems.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Električna struja." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table