polarogram → polarogram
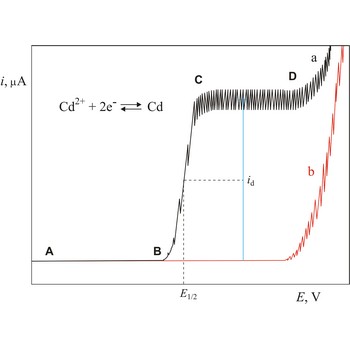
Polarogram is a graph of current versus potential in a polarographic analysis. The position of a polarographic wave in a polarogram along the x axis (E1/2) provides an identity of the substance while the magnitude of the limiting diffusion current (id) provides the concentration of this substance.
polarography → polarografija
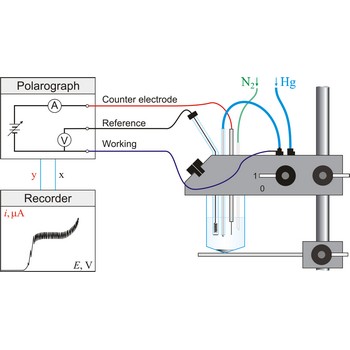
Polarography is a volumetric technique which is based on a diffusion controlled analyte travel to the surface of dropping mercury electrode (DME). The surface of the working electrode (dropping mercury electrode) is constantly renewed under dropping conditions and, thus, the conditions under which reaction takes place are readily reproducible. Depolarisation potential enables identification of ions present in the solution, and by measuring the diffusion current their concentration is calculated. Polarography was discovered in 1922 by the Czech chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský (1890-1967).
Schmidt number → Schmidtova značajka
Schmidt number (Sc) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where η is viscosity, ρ is density, and D is diffusion coefficient.
supercritical fluid extraction → superkritična fluidna ekstrakcija
Supercritical fluid extractions (SFE) have solvating powers similar to liquid organic solvents, but with higher diffusivities, lower viscosity, and lower surface tension. The main advantages of using supercritical fluids for extractions is that they are inexpensive, contaminant free, and less costly to dispose safely than organic solvents. For non-destructive isolation choose SFE, which is simply the best technology for sensitive raw materials. For these reasons supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is the reagent used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. Its gaslike behavior allows it to penetrate deep into the green coffee beans, and it dissolves from 97 % to 99 % of the caffeine present.
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
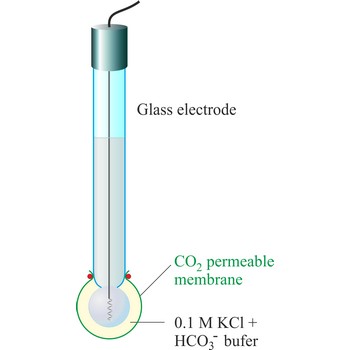
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Difuzija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table