reversible cell → povrativi članak
Reversible cell is an electrical cell the chemical action in which can be reversed by passing through it a current opposite in direction to that generated by the cell.
strong electrolyte → jaki elektrolit
Strong electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions completely dissociate into their ions. They conduct electric current very well.
transference number → prijenosni broj
Transference number of an ion is the fraction of the total current that is carried by that ion during electrolysis. Different ions carry different fractions of the current because different ions move at different speeds under the same potential gradient. In general, a cation and an anion differ in the amount of current they can carry during electrolysis.
electrolysis → elektroliza
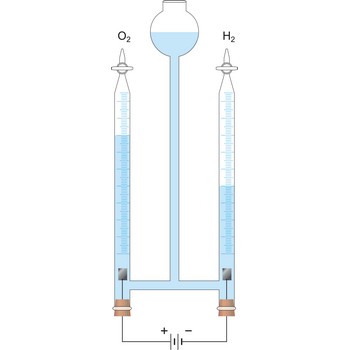
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a substance as a result of passing an electric current between two electrodes immersed in the sample.
electrolytes → elektroliti
Electrolytes are substances which, when melted or dissolved in water, conduct electric current. By melting or dissolving they are dissociated into electrically charged particles (ions) which are able to conduct electric current. By passing of electric current the transfer of matter occurs. Positively charged particles (cations) travel towards the negative pole (the cathode) and negatively charged particles (the anions) travel towards the positive pole (the anode). Liquid metals, in which the conduction is by free electrons, are not usually regarded as electrolytes. Solid conductors of ions, as in the sodium-sulphur cell, are also known as electrolytes. Depending upon how it conducts electric current, matter can be divided into strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes and nonconductors.
electrolytic cell → elektrolitska ćelija
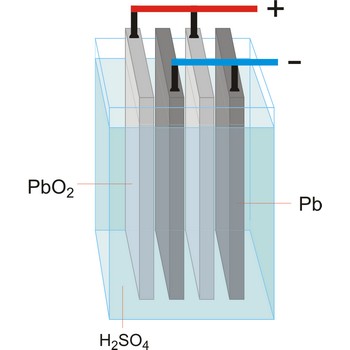
Electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously at the electrodes when they are connected through an external circuit. The reaction must be forced by applying an external electric current. It is used to store electrical energy in chemical form (rechargeable battery). It is also used to decompose or produce (synthesise) new chemicals by the application of electrical power. This process is called electrolysis, e.g., water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The free energy change of the overall cell reaction is positive.
Geiger counter → Geigerov brojač
Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller counter) is a device used to detect and measure ionising radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1 000 V is maintained between the electrodes. An ionising particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high potential will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionisations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882-1945). Geiger and W. Muller produced an improved design in 1928.
volt → volt
Volt (V) is the SI derived unit of electric potential. One volt is the difference of potential between two points of an electric conductor when a current of 1 ampere flowing between those points dissipates a power of 1 watt. It was named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745-1827).
voltametry → voltametrija
Voltametry is a common name for a large group of instrumental techniques which are based on measuring the electric current formed by a continuous potential shifting on the electrodes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Diffusion current." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table