acetal → acetal
Acetals are organic compounds having the structure R2C(OR’)2 (R’ ≠ H). They are organic compounds formed by addition of alcohol molecules to aldehyde or ketone molecules. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H ). Mixed acetals have different R’ groups. The formation of acetals is reversible; acetals can be hydrolysed back to aldehydes (ketone) in acidic solutions.
Acetal, 1,1-diethoxyethane (CH3CH(OC2H5)2), is an organic compound, pleasant smelling, formed by addition of ethyl alcohol to ethanal (acetaldehyde). It is used as a solvent and in synthetic organic chemistry.
acid-base titration → kiselo-bazna titracija
Acid-base titration is an analytical technique in volumetric analysis, where an acid of known concentration is used to neutralise a known volume of a base, and the observed volume of the acid required is used to determine the unknown concentration of the base. An acid-base indicator is used to determine the end-point of the titration.
substrate → supstrat
1. Substrate is a surface upon which an organism grows, sometimes by using chemicals of particles in the material as food
2. Substrate is a substance that is acted upon by an enzyme during a biochemical reaction.
3. Substrate is the material or product that is to be coated (for example, paint or laminate.).
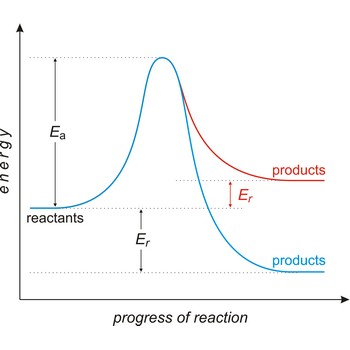
activation energy → energija aktivacije
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
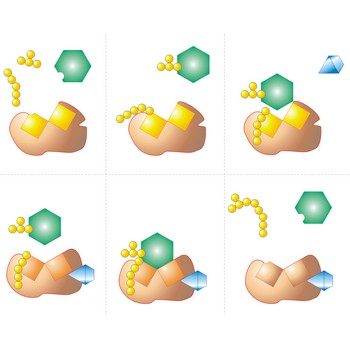
active site → aktivno mjesto
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
adenosine triphosphate → adenozin trifosfat
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is nucleotide that is of fundamental importance as a carrier of chemical energy in all living organisms. It consists of adenin linked to D-ribose).
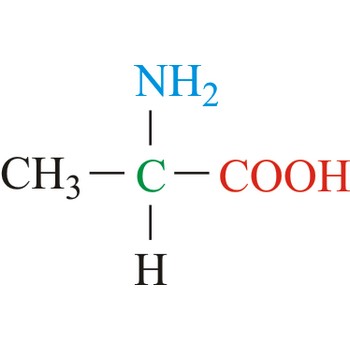
alanine → alanin
Alanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is the second simplest amino acid, but used the most in proteins. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be manufactured by the human body, and does not need to be obtained directly through the diet.
- Abbreviations: Ala, A
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2
- Molecular weight: 89.09 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Curtain rod width." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table