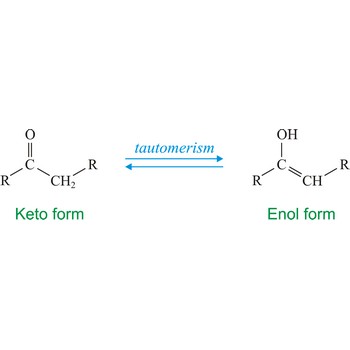
tautomerism → tautomerija
Tautomerism refers to equilibrium between two different structures of the same compound. Usually the tautomers differ in the point of attachment of a hydrogen atom. One of the most common examples of a tautomeric system is the equilibrium between a ketone (keto) and aldehyde (enol).
thermosetting plastic → termostabilna plastika
Thermosetting plastics (thermosets) refer to a range of polymer materials that cure, through the addition of energy, to a stronger form. The energy may be in the form of heat (rubber), through a chemical reaction (two part epoxy), or irradiation. Thermoset materials are usually liquid or malleable prior to curing, and designed to be molded into their final form, or used as adhesive.
Thermoset polymer resins transformed into plastics or rubbers by cross-linking into a rigid, 3-D structure. A thermoset material cannot be melted and re-molded after it is cured.
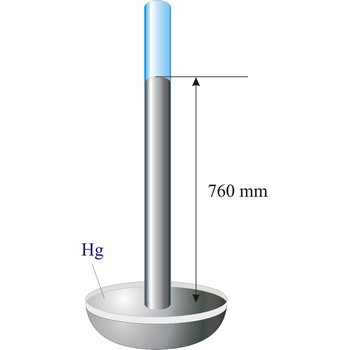
Torricelli, Evangelista → Torricelli, Evangelista
Evangelista Torricelli (1852-1908) is Italian physicist and mathematician. He became the first scientist to create a sustained vacuum and to discover the principle of a barometer. He filled a tube three feet long, and hermetically closed at one end, with mercury and set it vertically with the open end in a basin of mercury, taking care that no air-bubbles should get into the tube. The column of mercury invariably fell to about twenty-eight inches, leaving an empty space above its level. He discovered that the variation of the height of the mercury from day to day was caused by changes in the atmospheric pressure. He also constructed a number of large objectives and small, short focus, simple microscopes.
toxin → toksin
Toxins are effective and specific poisons produced by living organisms. They usually consist of an amino acid chain which can vary in molecular weight between a couple of hundred (peptides) and one hundred thousand (proteins). They may also be low-molecular organic compounds. Toxins are produced by numerous organisms, e.g., bacteria, fungi, algae and plants. Many of them are extremely poisonous, with a toxicity that is several orders of magnitude greater than the nerve agents. Botulinum toxin, produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, is the most poisonous substance known.
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
X-rays → X-zrake
X-rays are electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength than ultraviolet radiation (10-11 m to 10-9 m or 0.01 nm to 1 nm) produced by bombardment of atoms by high-quantum-energy particles. X-rays can pass through many forms of matter and they are therefore used medically and industrially to examine the internal structure.

zeolite → zeolit
Zeolite is a natural or synthetic hydrated aluminosilicate with an open three-dimensional crystal structure, in which water molecules are held in cavites in the latice. The water can be driven off by heating and the zeolite can then absorb other molecules of suitable size. Zeolites are used for separating mixtures by selective absorption.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Cubic close-packed structure." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table