unit cell → jedinična ćelija
Unit cell is the smallest fragment of the structure of a solid that by repetition can generate the entire structure.
urethane → uretan
Urethane is actually a misnomer as applied to polyurethane foam. It is a colorless, crystalline substance used primarily in medicines, pesticides, and fungicides. Urethane is not used in the production of urethane polymers or foams. The urethanes of the plastics industry are so named because the repeating units of their structures resemble the chemical urethane.
glucose → glukoza
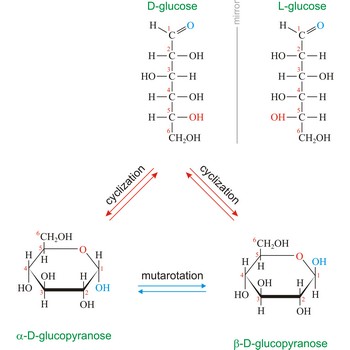
Glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar), C6H12O6, is an aldohexose (a monosaccharide sugar having six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group). An older common name for glucose is dextrose, after its dextrorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the right. Glucose in free (in sweet fruits and honey) or combined form (sucrose, starch, cellulose, glycogen) is is probably the most abundant organic compound in nature. During the photosynthesis process, plants use energy from the sun, water from the soil and carbon dioxide gas from the air to make glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is ultimately broken down to yield carbon dioxide and water, and the energy from this process is stored as ATP molecules (36 molecules of ATP across all processes).
Naturally occurring glucose is D isomers (OH group on the stereogenic carbon farthest from the aldehyde group, C-5, is to the right in the Fischer projection). Although often displayed as an open chain structure, glucose and most common sugars exist as ring structures. In the α form, the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the CH2OH attached to C-5 are located on opposite sides of the ring. β-glucose has these two groups on the same side of the ring. The full names for these two anomers of glucose are α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
vitamin → vitamin
The name vitamin is obtained from vital amines as it was originally thought that these substances were all amines. This is now known not to be true as vitamins have a range of structures. The body requires a small amout of vitamins, but any deficiency leads to metabolic and physical disorders.
X-ray diffraction pattern → rendgenski difrakcijski uzorci
X-ray diffraction pattern is an interference pattern created by x-rays as they pass through a solid material. Studying X-ray diffraction patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms.
homologous series → homologni niz
Series of compounds which have a common general formula and in which each member differs from the next member by a constant unit, which is the methylene group (-CH2-) is called the homologous series. Members of a homologous series are called homolog.
An example of the homologous series with some of their homologs are given below. Straight chain alkanes having general formula CnH2n+2
| Structure | Name |
|---|---|
| CH4 | methane |
| CH3-CH3 | ethane |
| CH3-CH2-CH3 | propane |
| CH3-CH2CH2CH3 | butane |
| CH3-(CH2)3-CH3 | pentane |
| CH3-(CH2)4-CH3 | hexane |
| CH3-(CH2)5-CH3 | heptane |
| CH3-(CH2)6-CH3 | octane |
| CH3-(CH2)7-CH3 | nonane |
| CH3-(CH2)8-CH3 | decane |
ion exchanger → ionski izmjenjivač
Ion-exchanger is a solid or liquid material containing ions that are exchangeable with other ions with a like charge that are present in a solution in which the material is insoluble. Ion-exchange resins consist of various copolymers having a cross-linked three-dimensional structure to which ionic groups have been attached.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Cubic close-packed structure." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table