Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
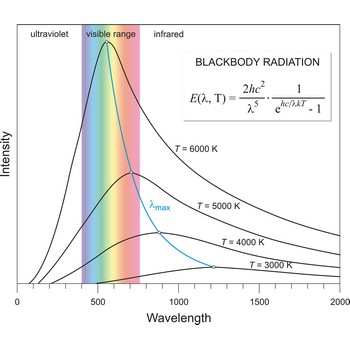
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
chain reaction → lančana reakcija
Chain reaction is a reaction done in three steps: initiation in which usually radicals are made which react with other molecules in stage of propagation and, when all reactants are spent, it ends by termination when all available radicals are completely spent.
Nuclear chain reaction refers to a process in which neutrons released in fission produce an additional fission in at least one further nucleus. Nuclear power plants operate by precisely controlling the rate at which nuclear reactions occur. On the other hand, nuclear weapons are specifically engineered to produce a reaction that is so fast and intense it cannot be controlled after it has started.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
chemical kinetics → kemijska kinetika
Chemical kinetics is an area of chemistry that studies rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions.
diffusion current → difuzijska struja
Diffusion current (id) is a current which is limited by the speed of particle diffusion in an electrolyte solution.
dynamic equilibrium → dinamička ravnoteža
Dynamic equilibrium is established when two opposing processes are occurring at precisely the same rate, so that there is no apparent change in the system over long periods of time.
chromatography → kromatografija
Chromatography is a method of separation of the components of a sample in which the components are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary while the other moves. In gas chromatography, the gas moves over a liquid or solid stationary phase. In liquid chromatography, the liquid mixture moves through another liquid, a solid, or a gel. The mechanism of separation of components may be adsorption, differential solubility, ion-exchange, permeation, or other mechanisms.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Brzina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table