electroanalytical chemistry → elektroanalitička kemija
Electroanalytical chemistry chemistry is the application of electrochemical cells and electrochemical techniques for chemical analysis. The analyte is dissolved in the electrolyte of the cell, and one can perform either qualitative analysis (determination of the type of constituents present) or quantitative analysis (determination of the amount of a given constituent).
crystal system → kristalni sustav
Crystal system is a method of classifying crystalline substances on the basis of their unit cell. There are seven unique crystal systems. The simplest and most symmetric, the cubic (or isometric) system, has the symmetry of a cube. The other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic.
|
Crystal system
|
Unit-cell
|
Conditions on unit-cell edges and angles |
|
cubic |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
|
hexagonal |
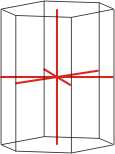 |
a≠c α=γ=90° β=120° |
|
tetragonal |
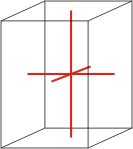 |
a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
rhombohedral |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
|
orthorhombic |
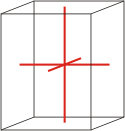 |
a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
monoclinic |
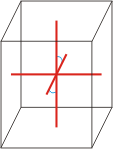 |
a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
|
triclinic |
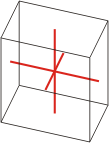 |
a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
equivalent → ekvivalent
Equivalent (eq) is a unit for describing the amount of a chemical species. In contrast to the mole, the amount of a substance contained in one equivalent can vary from reaction to reaction.
dialysis → dijaliza
Dialysis is a method by which large molecules (such as starch or protein) and small molecules (such as glucose or amino acids) may be separated in a solution by selective diffusion through a semipermeable membrane. Through this kind of membrane dissolved particles pass and colloid dimension particles fall behind. For example, if a mixed solution of starch and glucose is placed in a closed container made of a semipermeable substance (such as cellophane), which is then immersed in a beaker of water, the smaller glucose molecules will pass trough the membrane into the water, while the starch molecules remain behind.
diamagnetism → dijamagnetizam
In diamagnetism the magnetisation is in the opposite direction to that of the applied field, i.e. susceptibility is negative. It results from changes induced in the orbits of electrons in the atoms of a substance by the applied field, the direction of the change opposing the applied flux.
dielectric constant → dielektrična konstanta
Dielectric constant or permittivity (ε) is an index of the ability of a substance to attenuate the transmission of an electrostatic force from one charged body to another. The lower the value, the greater the attenuation. The standard measurement apparatus utilises a vacuum whose dielectric constant is 1. In reference to this, various materials interposed between the charged terminal have the following value at 20 °C:
| vacuum | 1 |
| air | 1.00058 |
| glass | 3 |
| benzene | 2.3 |
| acetic acid | 6.2 |
| ammonia | 15.5 |
| ethanol | 25 |
| glycerol | 56 |
| water | 81 |
The exceptionally high value for water accounts for its unique behaviour as a solvent and in electrolytic solutions. Dielectric constant values decrease as the temperature rises.
diffusion → difuzija
Diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of one substance with another when in contact or separated by a permeable membrane. Diffusion is a result of the random motions of their component atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles. Diffusion occurs most readily in gases, less so in liquids, and least in solids. The rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration of the substance and increases with temperature. The theoretical principles are stated in Fick’s laws.
dioxin → dioksin
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process, with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics, and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
dipole moment → dipolni moment
Electric dipole moment (μ) is a product of the positive charge and the distance between the charges. Dipole moments are often stated in debyes; The SI unit is the coulomb metre. In a diatomic molecule, such as HCl, the dipole moment is a measure of the polar nature of the bond; i.e. the extent to which the average electron charges are displaced towards one atom (in the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom). In a polyatomic molecule, the dipole moment is the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds. In a symmetrical molecule, such as tetrafluoromethane (CF4) there is no overall dipole moment, although the individual C-F bonds are polar.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Amfoterna tvar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table

