coal tar → ugljeni katran
Coal tar is a material obtained from the destructive distillation of coal in the production of coal gas. The crude tar contains a large number of organic compounds (e.g. benzene, naphthalene, methylbenzene, etc.), which can be separated by fractional distillation.
borane → borani
Borane is any of the group of compounds of boron and hydrogen (B2H6, B4H10, B5H9, B5H11...), many of which can be prepared by action of acid on magnesium boride (Mg3B2). Boranes are a remarkable group of compounds in that their structures cannot be described using the conventional two-electron covalent bond model.
boron → bor
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (England) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac (France) and L. J. Thenard (France). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks. It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. Combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color and in rockets as an igniter.
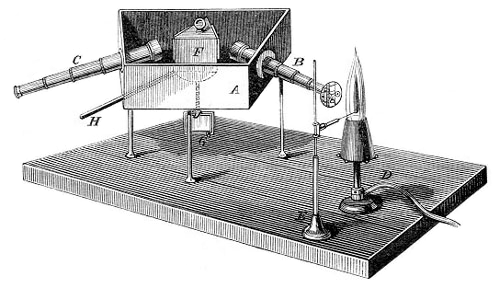
Bunsen, Robert Wilhem → Bunsen, Robert Wilhem
Robert Wilhem Bunsen (1811-1899) is a German chemist who held professorships at Kassel, Marburg and Heidelberg. His early researches on organometallic compound of arsenic cost him an eye in an explosion. Bunsen's most important work was in developing several techniques used in separating, identifying, and measuring various chemical substances. He also improvement chemical battery for use in isolating quantities of pure metals - Bunsen battery.
The essential piece of laboratory equipment that has immortalized the name of Bunsen was not invented by him. Bunsen improved the burner's design, which had been invented by Faraday, to aid his endeavors in spectroscopy. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the German physicist Gustav Kirchoff and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).
condensed structural formulas → kondenzirane strukturne formule
Condensed structural formulas are shortened and easier layout of structural formulas of organic compounds (butane, CH3(CH2)2CH3).
conjugated double bond → konjugirana dvostruka veza
Conjugated double bond in organic compounds is a system of double bonds between atoms which are separated by one single bond (1,3-butene, H2C=CH-CH=CH2).
covalent compound → kovalentni spoj
Covalent compound is a compound made of molecules - not ions, such as H2O, CH4, Cl2. The atoms in the compound are bound together by shared electrons. Also called a molecular compound.
cumulated double bond → kumulirana dvostruka veza
Cumulated double bond in organic compounds is a system of two double bonds on the same atom of carbon (C=C=C)
cyclization → ciklizacija
Cyclization is the formation of a cyclic compound from an open-chain compound.
cadmium → kadmij
Cadmium was discovered by Friedrich Strohmeyer (Germany) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cadmia meaning calamine (zinc carbonate, ZnCO3), or from the Greek word kadmeia with the same meaning. It is soft, malleable, blue-white metal. Tarnishes in air, soluble in acids, insoluble in alkalis. Boiling cadmium gives off a weird, yellow-colored vapour that is poisonous. Cadmium can cause a variety of health problems, including kidney failure and high blood pressure. Cadmium is obtained as a by product of zinc refining. The mayor use of cadmium is in electroplating of steel to protect it from corrosion. Also used to make nickel-cadmium batteries. The ability of cadmium to adsorb neutrons has made it of great importance in the design of nuclear reactors. Its compounds are found in paint pigments and a wide variety of intense colours.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Aliciklički spojevi." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table
