Results 471–480 of 1083 for Startseite Charts Anmelden Tools Schlagw%F6rter Mitgliederbereich language:en
diffraction → difrakcija
Diffraction is the ability of a wave to bend around the edges of obstacles or holes. The effect is most noticeable when the obstacle or hole is comparable to the size of the wavelength
dioxin → dioksin
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process, with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics, and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
dipole → dipol
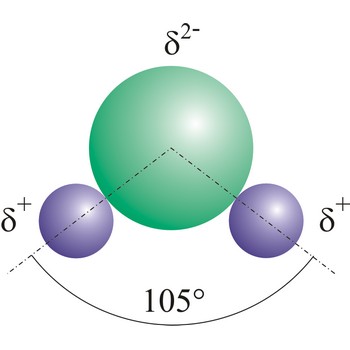
Dipole is a pair of separated opposite electric charges. Electric dipole is an assemblage of atoms or subatomic particles having equal electric charges of opposite sign separated by a finite distance. In the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom.
gravitational constant → gravitacijska konstanta
Gravitational constant (G) is the universal constant in the equation for the gravitational force between two particles
where r is the distance between the particles and m1 and m2 are their masses.
Grignard reagent → Grignardov reagens
Grignard reagents are organomagnesium halides, RMgX, having a carbon- magnesium bond (or their equilibrium mixtures in solution with R2Mg + MgX2).
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
dipole moment → dipolni moment
Electric dipole moment (μ) is a product of the positive charge and the distance between the charges. Dipole moments are often stated in debyes; The SI unit is the coulomb metre. In a diatomic molecule, such as HCl, the dipole moment is a measure of the polar nature of the bond; i.e. the extent to which the average electron charges are displaced towards one atom (in the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom). In a polyatomic molecule, the dipole moment is the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds. In a symmetrical molecule, such as tetrafluoromethane (CF4) there is no overall dipole moment, although the individual C-F bonds are polar.
disaccharide → disaharid
Disaccharides are compounds in which two monosaccharides are joined by a glycosidic bond. A glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon can be either α or β. For example, maltose, the disaccharide obtained by enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of starch, consists of two D-glucopyranose units joined by a 1,4’-α-glycoside bond. The "prime" superscript indicates that C-4 is not in the same ring as C-1. Unlike the other disaccharides, sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation because the glycosidic bond is between the anomeric carbon of glucose and the anomeric carbon of fructose.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Startseite Charts Anmelden Tools Schlagw%F6rter Mitgliederbereich language:en." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table