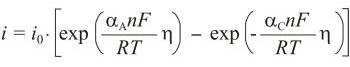Results 11–20 of 1083 for Startseite Charts Anmelden Tools Schlagw%F6rter Mitgliederbereich language:en
chemical element → kemijski element
Chemical element is a type of matter of which elementary matter is composed. Chemical element is composed of atoms with the same core charge.
chemical energy → kemijska energija
Chemical energy is the energy stored in substances and transferred during chemical reaction.
chemical engineering → kemijsko inženjerstvo
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that is concerned with the design, construction and operation of the plants and machinery used in industrial chemical processes.
chemical equation equalization → izjednačavanje kemijske jednadžbe
Chemical equation equalization is determining values of stechiometric coefficients of reactants and products in a chemical equation in a way that the number of atoms of each element is equal before and after the reaction.
complete ionic equation → potpuna ionska jednadžba
Complete ionic equation is a balanced equation that describes a reaction occurring in a solution, in which all strong electrolytes are written as dissociated ions.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
dynamic equilibrium → dinamička ravnoteža
Dynamic equilibrium is established when two opposing processes are occurring at precisely the same rate, so that there is no apparent change in the system over long periods of time.
ebullioscopic constant → ebulioskopska konstanta
Ebullioscopic constant (Eb) is the constant that expresses the amount by which the boiling point Tb of a solvent is raised by a nondissociating solute, through the relation
where b is the molality of the solute.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Startseite Charts Anmelden Tools Schlagw%F6rter Mitgliederbereich language:en." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table