electric field → električno polje
If a small amount of charge experience a force, there is an electric field in the vicinity. Electric field E is defined in terms of electrostatic force F that would be exerted on positive test charge qp placed in the field:
SI unit for electric field is N C-1, or V m-1.
The electric field due to a point charge q at distance r from it given by:
where ε0 is permittivity constant, and is εo=8.85×10-12 C2 N-1 m-2.
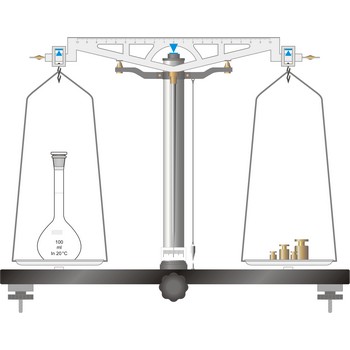
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
liquid crystal → tekući kristal
Liquid crystals or crystalline liquids are a physical state between crystals and melts. The liquid crystalline phase - the so-called mesophase - is formed at the melting point. The most important (usable) mesophases are nematic, cholesteric and smectic phase, having different molecular orientations.
low-weight fractions → lake frakcije
Low-weight (petroleum) fractions have low boiling points and short carbohydrates chains.
face-centered cubic lattice → plošno centrirana kubična rešetka
Face-centered cubic lattice (fcc or cubic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a =b =c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the fcc structures the spheres fill 74 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is four (8×1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4). There are 26 metals that have the fcc lattice.
face-centered orthorhombic lattice → plošno centrirana ortorompska rešetka
Face-centered orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
Fahrenheit scale → Fahrenheitova skala
Fahrenheit scale is the temperature scale in which 212 degrees is the boiling point of water and 32 degrees is the freezing point of water. The scale was invented in 1714 by the German physicist G.D. Fahrenheit (1686-1736).
32 °F = 0 °C
212 °F = 100 °C
1 °F =(5/9) °C
T(°C) = (5/9)[T(°F) - 32]
T(°F) = (9/5)T(°C) + 32
micelle → micele
Micelle is an electrically charged colloidal particle, usually organic in nature, composed of aggregates of large molecules, e.g., in soaps and surfactants. For aqueous solutions, the hydrophilic end of the molecule is on the surface of the micelle, while the hydrophobic end (often a hydrocarbon chain) points toward the centre.
ohm → om
Ohm (Ω) is the SI derived unit of electric resistance. The ohm is the electric resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant difference of potential of one volt, applied between these two points, produces in this conductor a current of one ampere, this conductor not being the source of electromotive force (Ω = V/A). The unit was named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm (1789-1854).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "ON POINT." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table