crystal → kristal
Crystal is a solid with a regular geometric shape, having a characteristic internal structure and enclosed by symmetrically arranged plane surfaces, intersecting at definite and characteristic angles. In crystals the particles (atoms, ions, or molecules) have a regular three-dimensional repeating arrangement in space. This is called the crystal structure. The crystal lattice is the arrangement of points in space at which the particles are positioned.
colloid ion → koloidni ion
Colloid ions emerge when colloid particles adsorb certain type of ion from solution and thus become charged with the same charge. The charge can also originate form a chemical reaction of colloid particle’s surface. Colloid ions formed by absorption of silver chloride particle can be show as follows:
Adsorbed layer is monomolecular (one molecule thick) and which type of ion will be formed depends upon which ions are present in a greater number in the solution in. Because of this colloid particles are charged with the same charge, mutual repelling occurs, and the colloid solution becomes stable. Colloid charge can be determined by electrophoresis.
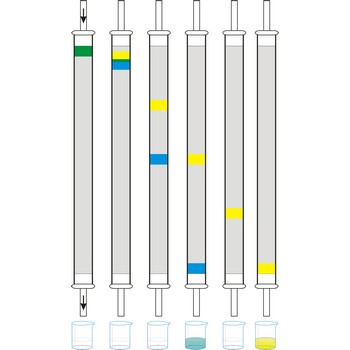
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
combustible → zapaljiv
The term combustible is often used to describe any material which will burn. However, conditions at which combustion will occur must be defined more accurately, for example a combustible liquid is 37.8 °C but below 93.3 °C. This allows a distinction to be made between combustible materials, which are fairly difficult to ignite, and flammable or highly flammable ones, which are far easier to ignite.
crystallisation → kristalizacija
Crystallisation is process in which the melted substance from a saturated solution turns into solid substance (crystal).
cyanide process → cijanidni postupak
Cyanide process is a method for separating a metal from an ore. Crushed ore is treated with cyanide ion to produce a soluble metal cyanide complex. The complex is washed out of the ore and reduced to metallic form using an active metal (usually zinc).
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "OFICINAVIRTUAL.ISSSTE.GOB.MX." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table