absorption → apsorpcija
Absorption is a phenomenon that occurs when matter crosses from one phase to another passing through the border surface and in the other phase more or less monotonously distributes itself in a concentration higher than the one within the first phase.
absorption coefficient → apsorpcijski koeficijent
Absorption coefficient (a) is the relative decrease in the intensity of a collimated beam of electromagnetic radiation, as a result of absorption by a medium, during traversal of an infinitesimal layer of the medium, divided by the length traversed.
abundance of substances → rasprostranjenost tvari
Abundance of substances is the ratio of the total mass of a specified element in the Earth’s crust to the total mass of the Earth’s crust. It is often expressed as a percentage.
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
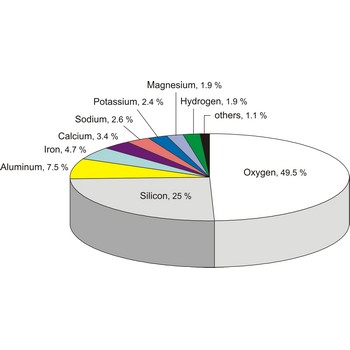
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
accelerated corrosion test → ubrzana korozija
Accelerated corrosion test is method designed to approximate, in a short time, the deteriorating effect under normal long-term service conditions.
accelerator → akcelerator
Accelerator is a device (machine) used for acceleration of charged particles (protons, deuterons, α-particles). Particles are accelerated under the influence of an electric field and with the help of a magnetic field are kept inside a certain space. When the particles reach enough acceleration (that is sufficient energy), they are directed on a target we wish to bomb. Best known types cyclotron, synchrotron, betatron.
Accelerator is a substance that increases the rate of chemical reaction, i.e. a catalyst.
acetal → acetal
Acetals are organic compounds having the structure R2C(OR’)2 (R’ ≠ H). They are organic compounds formed by addition of alcohol molecules to aldehyde or ketone molecules. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H ). Mixed acetals have different R’ groups. The formation of acetals is reversible; acetals can be hydrolysed back to aldehydes (ketone) in acidic solutions.
Acetal, 1,1-diethoxyethane (CH3CH(OC2H5)2), is an organic compound, pleasant smelling, formed by addition of ethyl alcohol to ethanal (acetaldehyde). It is used as a solvent and in synthetic organic chemistry.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "OFICINAVIRTUAL.ISSSTE.GOB.MX." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table