polarography → polarografija
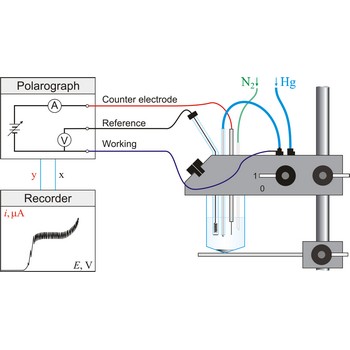
Polarography is a volumetric technique which is based on a diffusion controlled analyte travel to the surface of dropping mercury electrode (DME). The surface of the working electrode (dropping mercury electrode) is constantly renewed under dropping conditions and, thus, the conditions under which reaction takes place are readily reproducible. Depolarisation potential enables identification of ions present in the solution, and by measuring the diffusion current their concentration is calculated. Polarography was discovered in 1922 by the Czech chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský (1890-1967).
polonium → polonij
Polonium was discovered by Marie Curie (Poland) in 1898. Named for Poland, native country of Marie Curie. It is silvery-grey, extremely rare, radioactive metal. Soluble in dilute acids. Highly toxic. Severe radiotoxicity. Carcinogen. Polonium occurs in pitchblende. Produced by bombarding bismuth with neutrons. Used in industrial equipment that eliminates static electricity caused by such processes as rolling paper, wire and sheet metal.
standing wave → stojni val
Standing waves occur when a travelling wave reflects from the fixed ends of a string, producing other waves moving in opposite direction. They are called standing waves because the energy in the string cannot move past the fixed ends, i.e. it stands in the string. In real strings, after some time, standing waves are eventually damped due to friction.
stereospecific reaction → stereospecifična reakcija
Stereospecific reactions are reactions that proceed predominantly to a single stereoisomeric product out. All metabolic conversions involving chiral molecules are stereospecific.
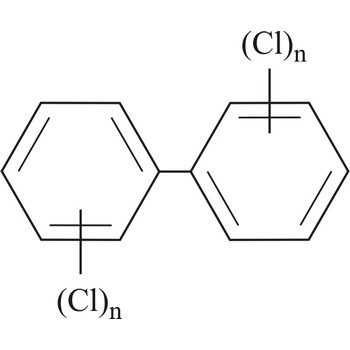
polychlorinated biphenyls → poliklorirani bifenili
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) are poisonous and carcinogenic compounds. They are pollutants of both live and inanimate environment, and they are used as insulation and refrigerating materials in transformers and condensers.
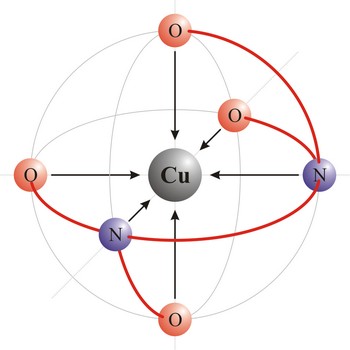
polydentant ligand → polidentantni liganad
Polydentant ligands contain more co-ordination points (can give more electron pairs) and they form complex ringlike structures (celate complexes) by replacing two or more monodentant ligands. That kind of ligand is EDTA which has 6 co-ordinational points and with metals it creates complexes, always in 1:1 ratio.
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
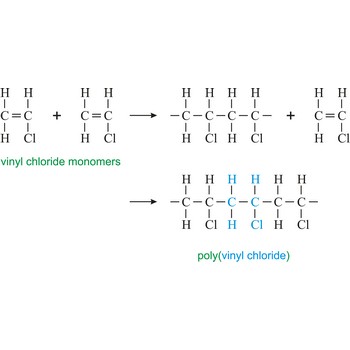
polymerization → polimerizacija
Polymerization is a reaction of connecting many monomers in one long molecule whereby polymers are created.
Strouhal number → Strouhalova značajka
Strouhal number (Sr) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where l is length, f is frequency, and v is velocity.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "OFICINAVIRTUAL.ISSSTE.GOB.MX." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table