absolute zero → apsolutna nula temperature
Absolute zero is theoretically, the lowest attainable temperature. It is the energy at which the kinetic energy of atom and molecules is minimal and is equivalent to -273.15 °C.
absorbed dose → apsorbirana doza
For any ionising radiation, absorbed dose (D) is the mean energy imparted to an element of irradiated matter divided by the mass of that element.
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
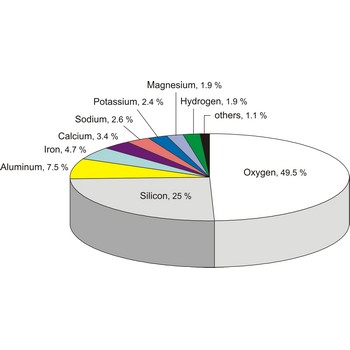
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
accelerator → akcelerator
Accelerator is a device (machine) used for acceleration of charged particles (protons, deuterons, α-particles). Particles are accelerated under the influence of an electric field and with the help of a magnetic field are kept inside a certain space. When the particles reach enough acceleration (that is sufficient energy), they are directed on a target we wish to bomb. Best known types cyclotron, synchrotron, betatron.
Accelerator is a substance that increases the rate of chemical reaction, i.e. a catalyst.
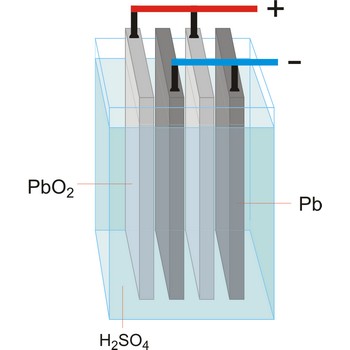
accumulator → akumulator
Accumulator (secondary cell, storage battery) is a type of voltaic cell or battery that can be recharged by passing current through it from an external D.C. supply. The charging current reverses the chemical reactions in the cell. The common types are the lead-acid accumulator and the nickel-cadmium cell.
activated complex → aktivirani kompleks
Activated complex is an intermediate structure formed in the conversion of reactants to products. The activated complex is the structure at the maximum energy point along the reaction path; the activation energy is the difference between the energies of the activated complex and the reactants.
biogas → bioplin
Biogas is a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide resulting from the anaerobic decomposition of such waste materials as domestic, industrial, and agricultural sewage. Methanogenic bacteria carry out the decomposition; these obligate anaerobes produce methane, the main component of biogas, which can be collected and used as an energy source for domestic processes, such as heating, cooking, and lighting.
chemiluminescence → kemiluminiscencija
Chemiluminescence is energy release in form of electromagnetic radiation during a chemical reaction.
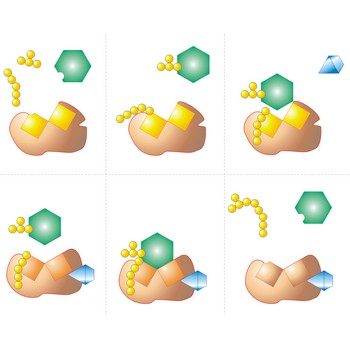
active site → aktivno mjesto
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Helmholzova slobodna energija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table