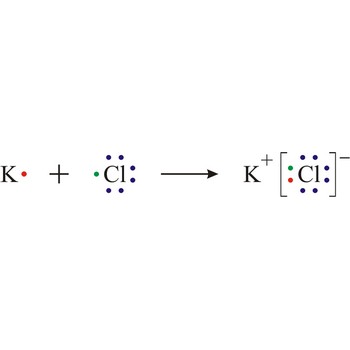ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
X-ray spectrum → spektar X-zraka
X-ray spectrum is a set of characteristic X-ray frequencies or wavelengths produced by a substance used as a target in an X-ray tube. Each element has a characteristic X-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number and the frequencies of certain lines in the X-ray spectrum.
lanthanides → lantanoidi
Lanthanides (lanthanons, lanthanoids or rare-earth elements) are a series of fourteen elements in the periodic table, generally considered to range in proton number from cerium to lutetium inclusive. It was convenient to divide these elements into the cerium group or light earth: cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu); and the yttrium group or heavy earths: gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb) i lutetium (Lu). The position of lanthanum is somewhat equivocal and, although not itself a lanthanide, it is often included with them for comparative purpose. The lanthanides are sometimes simply called the rare earths. Apart from unstable Pm, the lanthanides are actually not rare. Cerium is the 26. most abundant of all elements, 5 times as abundant as Pb. All are silvery very reactive metals.
period → perioda
Periods are horizontal rows in the periodic table, each period begin with an alkali metal (one electron in the outermost principal quantum level) and ending with a noble gas (each having eight electrons in the outermost principal quantum level, except for helium, which is limited to two).
periodic table of the elements → periodni sustav elemenata
Periodic table is a table of elements, written in sequence in the order of atomic number or atomic weight and arranged in horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups) to illustrate the occurrence of similarities in the properties of the elements as a periodic function of the sequence. The original form was proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, using relative atomic masses.
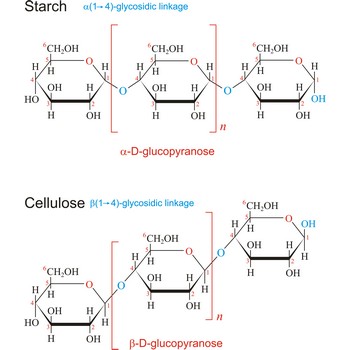
polysaccharide → polisaharid
Polysaccharides are compounds consisting of a large number of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked together by glycosidic bonds. When polysaccharides are composed of a single monosaccharide building block, they are termed homopolysaccharides. Heteropolysaccharides contain two or more different types of monosaccharide. Polysaccharides may have molecular weights of up to several million and are often highly branched. Since they have only the one free anomeric -OH group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show noticeable mutarotation. The most common polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
significant figures → značajne znamenke
Measurements are not infinitely accurate: we must estimate measurement uncertainty. The number of significant figures is all of the certain digits plus the first uncertain digit.
Rules for significant figures:
- Disregard all initial zeros.
- Disregard all final zeros unless they follow a decimal point.
- All remaining digits including zeros between nonzero digits are significant.
| 0.0023 | has two significant figures |
| 0.109 | has three significant figures |
| 2.00 | has three significant figures |
| 70 | has one significant figure |
In addition and subtraction, the number of significant figures in the answer depends on the original number in the calculation that has the fewest digits to the right of the decimal point.
In multiplication and division, the number of significant figures in a calculated result is determined by the original measurement that has the fewest number of significant digits.
In a logarithm of a number, keep as many digits to the right of the decimal point as there are significant figures in the original number.
In an antilogarithm of a number, keep as many digits as there are digits to the right of the decimal point in the original number.
wavenumber → valni broj
Wavenumber is the number of wave cycles per unit distance.
There are unfortunately two different definitions of the wavenumber.
Wavenumber, k, is most frequently defined as
with wavelength λ, phase velocity of wave vp, and angular frequency ω.
Less frequently it is defined simply as
One must be careful to note which definition is in use. Wavenumbers are used extensively in infrared spectroscopy, and usually have units of cm-1.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Geigerov brojač." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table