spectroscopy → spektroskopija
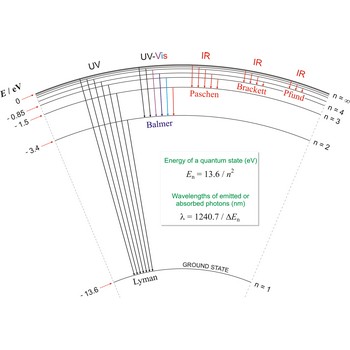
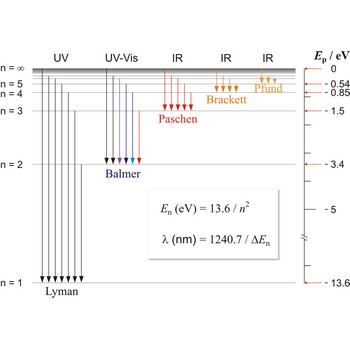
Spectroscopy is the analysis of the lines of light emitted from excited atoms as the electrons drop back through their orbitals. These lines give the energy and distances of the electronic orbitals.
X-ray spectrum → spektar X-zraka
X-ray spectrum is a set of characteristic X-ray frequencies or wavelengths produced by a substance used as a target in an X-ray tube. Each element has a characteristic X-ray spectrum, and there is a strong correlation between atomic number and the frequencies of certain lines in the X-ray spectrum.
Kirchoff, Gustav → Kirchoff, Gustav
Gustav Kirchoff (1824-1887) was a German physicist who, with the chemist Robert Bunsen (1811-1899), laid the foundations of spectral analysis. He realized that the Fraunhofer lines in the Sun's spectrum were due to light from the photosphere being absorbed at those specific wavelengths by elements in the solar atmosphere. He also found that incandescent solids, liquids, and compressed gases emit a continuous spectrum. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the Bunsen and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).
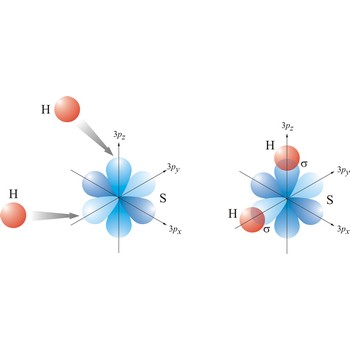
linear molecular geometry → linearna geometrija molekule
Linear molecule is a molecule in which atoms are deployed in a straight line (under 180° angle). Molecules with an linear electron pair geometries have sp hybridization at the central atom. An example of linear electron pair and molecular geometry are carbon dioxide (O=C=O) and beryllium hydride BeH2.
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
Zeeman, Pieter → Zeeman, Pieter
Pieter Zeeman (1865-1943) was a Dutch physicist who discovered the splitting of the spectral lines of a substance when placed in a magnetic field (known as the Zeeman effect). In 1902, Zeeman and Lorentz were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics, for their, extraordinary service they rendered by their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomenon.
sigma bond → sigma veza
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
structural formula → strukturna formula
Structural formula is a two dimensional representations of the arrangement of the atoms in molecules. Atoms are represented by their element symbols and covalent bonds are represented by lines. The symbol for carbon is often not drawn.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "D-linije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table