heterocyclic compounds → heterociklički spojevi
Heterocyclic compounds are cyclic compounds having as ring members atoms of at least two different elements, e.g., quinoline, 1,2-thiazole.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
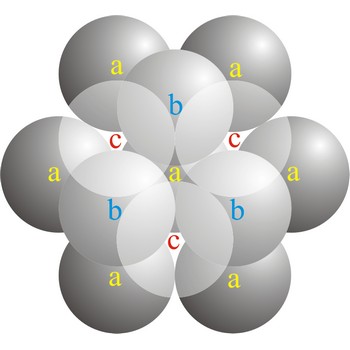
cubic close-packed structure → kubična gusta slagalina
In a cubic close-packed (ccp) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of four layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers (a) contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The atoms in the second layer (b) fit into depressions in the first layer. The atoms in the third layer (c) occupy a different set of depressions than those in the first. The cubic close packed structure can be made by piling layers in the a-b-c-a-b-c-a-b-c... sequence.
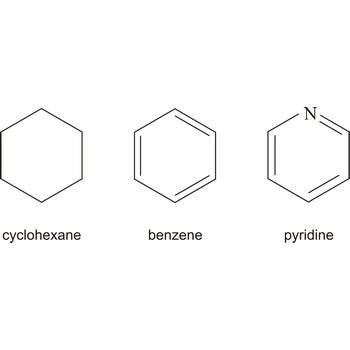
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
ionisation energy → energija ionizacije
Ionisation energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom or molecule (in its vibrational ground state) in the gaseous phase.
isoelectronic → izoelektronske čestice
Isoelectronic refers to a group of atoms or ions having the same number of electrons. For example, F-, Ne, and Na+ are isoelectronics.
decay series → raspadni niz
Decay series is a series of decay in which radioactive element is decomposed in different elements until it produces one stable atom.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Chaotic Atoms (Dramatic)." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table