nonpolar molecule → nepolarna molekula
Nonpolar molecule is a molecule which has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are formed. For example, the Cl2 molecule has no polar bonds (molecule with one type of atom), CH4 is a non-polar molecule (due to its symmetry). Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve in water as they cannot form hydrogen bonds (thus are hydrophobic) but do dissolve in lipids or fats (lipophilic).
nuclear magnetic resonance → nuklearna magnetska rezonancija
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a type of radio-frequency spectroscopy based on the magnetic field generated by the spinning of electrically charged atomic nuclei. This nuclear magnetic field is caused to interact with a very large (1 T - 5 T) magnetic field of the instrument magnet. NMR techniques have been applied to studies of electron densities and chemical bonding and have become a fundamental research tool for structure determinations in organic chemistry.
octahedral molecular geometry → oktaedarska geometrija molekule
Octahedral molecular geometry (square bipyramidal shape) describes the shape of compounds where six atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom. The sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), with six bonding pairs, is predicted and found to be a regular octahedron. Four of the attachments are positioned in a square plane with 90° bond angles. The remaining two attachments are positioned perpendicular (90°) to the square plane at opposite ends of the central atom. Molecules with an octahedral electron pair geometries have sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybridization at the central atom.
octet rule → pravilo okteta
Octet rule states that the chemical properties of the elements repeat on a regular basis with increasing atomic mass, and that the chemical properties of each eight element are similar. Since the inert gases, with the exception of helium have eight electrons in their outer shells, this stable electronic configuration is called the octet rule. In chemical reactions atoms of elements tend to react in such a way as to achieve the electronic configuration of the inert gas nearest to them in the periodic table. There are a number of exceptions to the octet rule.
omega-3 fatty acids → omega-3 masne kiseline
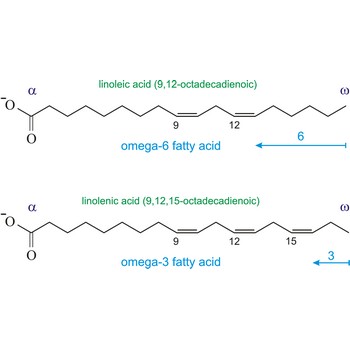
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning they contain more than one double bond. The name omega-3 indicates that the first double bond occurs on the third carbon atom (n-3) from the methyl (-CH3) end of the molecule (omega position). The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3). ALA comes from plants. EPA and DHA come from fish.
Similarly, the first double bond in omega-6 fatty acids is located between the sixth and seventh carbon atom (n-6) from the methyl end of the fatty acid (omega end).
orbital → orbitala
Orbital is the area in space about an atom or molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is greatest.
The possible atomic orbitals correspond to subshells of the atom. Thus there is one s-orbital for each shell (orbital quantum number l = 0). There are three p-orbitals (corresponding to the three values of l) and five d-orbitals. The shapes of orbitals depend on the value of l.
oxidation number → oksidacijski broj
Atoms can give one or more electrons for bond forming. The valence of any atom, which comes from stechiometrical relation of interbonded atoms, is called an oxidation number or an oxidation degree. Oxidation number of atoms in elementary state is zero. An atom of greater electronegativity has a negative, and an atom of lesser electronegativity has a positive oxidation number.
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
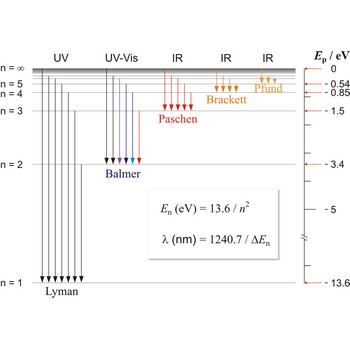
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
peptide bond → peptidna veza
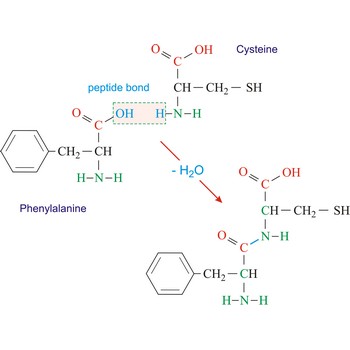
Peptide bond emerges when two amino acid join in a way that the carbon atom from one connects with the nitrogen atom from the other (creating a C-N bond).
periodic table of the elements → periodni sustav elemenata
Periodic table is a table of elements, written in sequence in the order of atomic number or atomic weight and arranged in horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups) to illustrate the occurrence of similarities in the properties of the elements as a periodic function of the sequence. The original form was proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, using relative atomic masses.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Chaotic Atoms (Dramatic)." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table