aqua regia → zlatotopka
Aqua regia is a mixture of one volume part of nitric acid (HNO3) and three volume parts of hydrochloric acid (HCl). Dissolving of gold in aqua regia is described by the following equation:
aqueous solution → vodena otopina
Aqueous solutions are those solutions where water is the solvent. An aqueous solution found in an equation describing a chemical reaction is denoted by the state symbol, (aq).
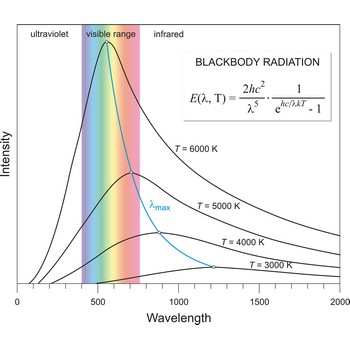
blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
chemical reaction → kemijska reakcija
Chemical reaction is a change of chemical properties of substances which react with each other. By means of a chemical reaction new substances are created by bond breaking between atoms and molecules of reactants and their reuniting in a new way, thereby creating products. Chemical reactions can be shown by chemical equations.
chemical symbols → kemijski simboli
Chemical symbols are a derived way of showing elements in a formula or equation. Each symbol represents one atom and it usually consists of the first two letters of the Greek or Latin name of the element.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
Charles’ law → Charlesov zakon
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure expand by the constant fraction of its volume at 0 °C. For each Celsius or kelvin degree its temperature is raised. For any ideal gas fraction it is approximately 1/273. This can be expressed by the equation
were V° is the volume at 0°C and V is its volume at t°C.
This is equivalent to the statement that the volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure is proportional to its thermodynamic temperature
This law also know as Gay-Lussac’s law.
An equation similar to the one given above applies to pressures for ideal gases:
elementary reaction → elementarna reakcija
Elementary reaction is a reaction that occurs in a single step. Equations for elementary reactions show the actual molecules, atoms, and ions that react on a molecular level.
gravitational constant → gravitacijska konstanta
Gravitational constant (G) is the universal constant in the equation for the gravitational force between two particles
where r is the distance between the particles and m1 and m2 are their masses.
reaction order → red reakcije
Order of a reaction (n) is the sum of the exponents of the concentration terms in a rate equation.
Total order of a reaction is
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Arheniusova jednadžba." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table