Torricelli, Evangelista → Torricelli, Evangelista
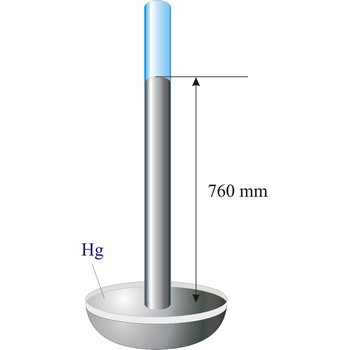
Evangelista Torricelli (1852-1908) is Italian physicist and mathematician. He became the first scientist to create a sustained vacuum and to discover the principle of a barometer. He filled a tube three feet long, and hermetically closed at one end, with mercury and set it vertically with the open end in a basin of mercury, taking care that no air-bubbles should get into the tube. The column of mercury invariably fell to about twenty-eight inches, leaving an empty space above its level. He discovered that the variation of the height of the mercury from day to day was caused by changes in the atmospheric pressure. He also constructed a number of large objectives and small, short focus, simple microscopes.
toxin → toksin
Toxins are effective and specific poisons produced by living organisms. They usually consist of an amino acid chain which can vary in molecular weight between a couple of hundred (peptides) and one hundred thousand (proteins). They may also be low-molecular organic compounds. Toxins are produced by numerous organisms, e.g., bacteria, fungi, algae and plants. Many of them are extremely poisonous, with a toxicity that is several orders of magnitude greater than the nerve agents. Botulinum toxin, produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, is the most poisonous substance known.
tryglyceride → triglicerid
Triglyceride is an ester of glycerol and three fatty acids. It is the main constituent of vegetable oil and animal fats. The fatty acids attached to the glycerol can be the same or different. Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals are typically composed only of even numbers of carbon atoms (usually from 16 to 20) due to the way they are bio-synthesized from acetyl CoA.
U-tube manometer → U-manometar
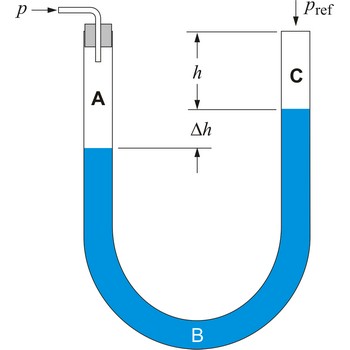
U-tube manometer contains water or mercury in a U-shaped tube, and is usually used to measure gas pressure. One end of the U tube is exposed to the unknown pressure field (P) and the other end is connected to a reference pressure source (usually atmospheric pressure) (Pref), shown in the schematic below.
If fluid C is the atmosphere, fluid B is the liquid in the U tube (e.g. water or mercury), and fluid A is a gas, then we can assume that ρB >> ρA, ρC. The pressure contributed by the weight of gas within the U tube can therefore be neglected. The gage pressure of the gas can be approximated by,
water → voda
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
Wohler’s synthesis → Wohlerova sinteza
Wöhler’s synthesis is a synthesis of urea performed by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler (1800-1882) in 1828. He discovered that urea (CO(NH2)2) was formed when a solution of ammonium isocyanate (NH4NCO) was evaporated. At the time it was believed that organic substances such as urea could only be made by living organisms, and its production from an inorganic compound was a notable discovery.
Schrotter apparatus for determination of CO2 → Schrotterova aparatura za određivanje CO2
Schrötter decomposition apparatus (Schrötter's alkalimeter) is used to determining the carbonate content in samples of limestone, gypsum, dolomite, or baking powder by loss of weight. The apparatus is named after the Austrian chemist Anton Schrötter von Kristelli (1802-1875), who devised it in 1871. The size of the filled apparatus (apparatus is 16 cm high) is such that it weights less than 75 g, and can be placed on the pan of an analytical balance.
Procedure: Weigh about 0.5 g of the powdered carbonate sample and introduce it into the decomposition flask C. Pour into the drying tube A 2-3 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and to the dropping funnel B add about 10-15 mL of hydrochloric acid (w(HCl) = 15 %). Weigh the whole apparatus. Open the upper taps of both parts and allow the hydrochloric acid from B to run slowly down on to the powdered sample. The evolved CO2 escapes through the strong sulphuric acid and is thus thoroughly dried. When further addition of acid produces no more evolution of CO2, warm the apparatus up to 80 °C so as to expel the CO2 from the solution. Connect the upper tap of the drying tube A to a water pump and draw a slow current of air through the apparatus until completely cool. Open the upper taps for a moment to equalize the internal and external pressure and weight the apparatus again. The weight loss is equal to the weight of carbon dioxide liberated from the carbonates.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "živo vapno." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table